Business Loan Broker Shamed on TV by Investigative Reporter
January 5, 2018A business loan broker found himself on the wrong end of Television fame this week when award-winning investigative reporter Arnold Diaz showed up at his office to question him about fees charged to merchants for loans he did not procure. The exchange, which was captured on camera and broadcast on WPIX-11 in New York, shows Bridgehampton Funding managing director Anthony Kline of Long Island, initially running away when confronted about the allegations.
Kline and Bridgehampton are accused of charging merchants upfront fees to get them loans, failing to get the loans, and then keeping the fees. Bridgehampton also allegedly used LOIs of a real commercial lender’s letterhead to lure merchants into believing that a loan would be forthcoming. But the LOIs are forged, according to one commercial lender that has filed a lawsuit for fraud against Kline and his firm, swearing that they have no business relationship. Trevor Cole Commercial Co of CT, the plaintiff, is seeking more than $1 million in damages.
The alleged scheme is similar to other forged LOI scams that have been reported to AltFinanceDaily by lenders hesitant to go on the record with the names of the offending brokers.
Bridgehampton Funding’s website claims they offer everything from merchant cash advances to SBA loans to equipment leasing.
Banks Set Sights on Small Business Loans Under $100,000
December 13, 2017BOSTON – One of the oldest lenders in the nation had a hand in developing technology intended to enable banks to win back the small business loan market from alternative lenders.
A tech incubator at Boston-based Eastern Bank, founded in 1818, has spun off Numerated Growth Technologies Inc., a startup that developed an online platform designed to identify and contact small businesses eligible for loans of up to $100,000.
Numerated Growth, which was founded in March, developed its tech in Eastern Labs and has generated about $100 million of volume since 2015. The model, which features real-time approval, is based on the tact banks first took with pre-approved credit cards in the 1990s, Numerated CEO Dan O’Malley told AltFinanceDaily.
“We’re just taking the same rules and applying them here,” he said. “And by the way, that’s what customers want.”
Numerated Growth, which employs 26 workers, came out of stealth mode in May with a $9 million seed funding.

O’Malley, Eastern Bank’s former chief digital officer, said Numerated is now selling the platform to other banks but declined to disclose the specific number. The cost per bank depends on the number of loans being processed, he said.
The average business loan is $40,000 and they can be approved and funded within five minutes of the business completing the online agreement.
Numerated Growth’s real-time platform could be considered loan origination software on steroids. But such software essentially enables a bank to enter an applicant’s information into a digitized system to assist in the approval process. Alternative lending startups have been improving on that model for several years. Competitors in that space include nCino Inc., Decision Lender (Teledata Communications), PerfectLO and defi solutions, LoanCirrus.
But loan origination software is very crowded and startups are constantly launching to reduce the time it takes to approve a loan without increasing the number of defaults.
 “Banks need to do things that are counter to each other,” David O’Connell, a senior analyst for the Boston-based Aite Group LLC, told AltFinanceDaily. “There’s a need to do a fast money transaction, but doing it diligently without making any bad loans.”
“Banks need to do things that are counter to each other,” David O’Connell, a senior analyst for the Boston-based Aite Group LLC, told AltFinanceDaily. “There’s a need to do a fast money transaction, but doing it diligently without making any bad loans.”
Combining the marketing and approval process is a credible approach because it keeps them on the same page in terms of targeting the most likely prospects. As a result, the number of “false positives” is lower, O’Connell said.
Instead of developing their own small business loan platforms, some banks are referring borderline borrowers to alternative lenders. But that can cause problems for the bank if the customer service doesn’t measure up to the bank’s standards and customers associate shoddy service with the entity that referred them, O’Connell said.
The best option is to develop in house. “Banks need to go as deep into the alternative lending market as they can with their own infrastructure and brand,” he said.
Because of its low value compared with other types of bank business, small business loan origination is one of the last remaining areas of banking to be targeted with innovation. “There’s not a huge price point,” said Kevin Tweddle, executive vice president for innovation and technology at the Independent Community Bankers of America.
Loan origination startups are trying to make such deals worth the bother. Yet the best tools tend to be developed by banking industry people because they understand the regulatory restrictions and integration factors, he said.
The goal of loan tech tools is two-pronged: make the approval process more efficient and make it convenient for borrowers. And so far, no software developer has risen above all the others to capture majority market share, Tweddle told AltFinanceDaily.
“It’s just too early; there’s too many of them still coming out,” he said. “We’re in the early innings of a nine-inning game.”
Market metrics
Banks can’t afford to ignore the demand for alternative lending tools.
In May, the University of Chicago’s Polsky Center for Entrepreneurship and Innovation reported that the alternative finance market slowed but continued to grow during 2016 in the United States, Canada, Latin America and the Caribbean. The market’s value reached $35.2 billion — a 23 percent increase compared with 2015.
More than 200,000 businesses used online alternative funding sources during 2016. In the United States, marketplace and peer-to-peer consumer lending accounted for the largest share of market volume with $21 billion in the U.S. last year, a 17 percent increase. Balance sheet business lending was the second-largest model in the U.S. with $6 billion originated, the report found.
In Latin America and the Caribbean, marketplace and peer-to-peer business lending was the largest alternative finance segment with $188.5 million last year, a 239 percent rise versus 2015.
The same principles fueling the car-sharing business are being applied to peer-to-peer lending. As a result, adoption is growing as people view the credibility of peer lenders on an equal level of traditional experts, said David Wong, senior director of the innovation and acceleration lab at the Chicago-based CME Group Inc.
“Whether P2P markets reach or exceed the size of the incumbent market platforms (ala Uber and Airbnb), or not, they are driving rapid innovation and new dimensions of competition across industries,” he said.
Early adoption
Industry observers agree that small business loans haven’t seen enough innovation from the banking industry because of its size compared with commercial lending and real estate deals. As a result, it has a long way to go to shorten the time it takes for approvals and improving the customer experience, O’Connell said.
“Banks that fail to embrace automation for their commercial lending lines of business will lose the valuable relationships, loan outstandings, and fee-based income abundant in the commercial and industrial market,” he said.
 After the 2009 global financial crisis, bank regulations tightened and data sets were required to be available and analytics-ready, providing another compelling need for commercial loan origination systems, O’Connell said.
After the 2009 global financial crisis, bank regulations tightened and data sets were required to be available and analytics-ready, providing another compelling need for commercial loan origination systems, O’Connell said.
No dominant players have emerged because neither traditional banks nor alternative lenders have figured out the best approach that satisfies both the lender and the customer, O’Connell said.
“Businesses don’t want money right away but they do want a quick and easy process,” he said. “My data tells me that in addition to providing underwhelming turnaround time, no particular lender has an edge over another. Nobody has it right.”
At Numerated Growth, O’Malley said the “initial wake-up call” signaling that a change was needed came in 2013 when Eastern Bank noticed solid small business customers paying off loans from alternative lenders such as On Deck Capital Inc. and LendingClub Corp. The pattern suggested that there was an unmet customer need.
Numerated Growth’s platform is designed to enable banks to proactively aggregate the data they need to identify prospective borrowers instead of requiring business owners to collect the data and present it to banks, O’Malley said.
“We’re making the banks do the work,” he said. “The same process that transformed the credit card industry will transform the financial products industry.”
6th Avenue Capital Secures $60 Million Commitment For Merchant Cash Advance Funding
November 2, 2017Highly Experienced Executive Team Offers Flexible Financing Options to Small Businesses
New York City – November 2, 2017 – 6th Avenue Capital, LLC (“6th Avenue Capital”), a leading provider of small business financing solutions, announced today its securement of a $60 million commitment from a large institutional investor. The investor made their commitment based on 6th Avenue Capital’s industry-leading underwriting, compliance standards and processes. 6th Avenue Capital will draw from this commitment to offer merchant cash advances to small businesses through its nationwide network of Independent Sales Organizations (“ISOs”) and other strategic partnerships, such as banks and small business associations.
6th Avenue Capital launched formal operations in 2016 to help finance small businesses that are often ineligible for funding due to traditional underwriting criteria. 6th Avenue Capital evaluates each application for funding individually and keeps the merchant’s short and long-term needs in mind including, most importantly, what they can afford. 6th Avenue Capital also understands that small businesses may need funding quickly. The company’s data-driven underwriting processes, expertise and technology can give the merchant secure and equitable approvals of qualified requests and funding within hours.
Leading the team, CEO Christine Chang oversees all strategic aspects of 6th Avenue Capital. She also serves as COO to sister company Nexlend Capital Management, LLC. She brings more than 20 years experience in institutional asset management, including alternative lending. Previously, Chang served as Chief Compliance Officer at Alternative Investment Management, LLC, COO at New York Private Bank & Trust and Vice President at Credit Suisse. She serves on the board of Blueprint Capital Advisors, LLC and Bottomless Closet, a not-for-profit empowering economic self-sufficiency in disadvantaged NYC women.
“Our mission at 6th Avenue Capital is to help small businesses grow, and we continue to expand our existing network of ISO and strategic partners to ensure these businesses have access to capital in hours,” said Chang. “Our leadership team of financial industry experts has extensive experience navigating multiple economic cycles. We know how to serve merchants and how to deliver quickly while meeting the highest operational standards for our investors.”
COO Darren Schulman joined the team in March 2017. Schulman is a 20-year veteran of the alternative finance and banking industries. He is responsible for oversight of 6th Avenue Capital’s origination, underwriting, operations and collections, as well as strategic initiatives. Schulman served previously as COO at Capify (formerly AmeriMerchant), a global small business financing company, and President and CFO at MRS Associates, a Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) company specializing in collections. In addition, Schulman was an Executive Vice President at MTB Bank.
“We form strong relationships with the merchant and consider it essential for our underwriters to speak to every merchant, on every deal, regardless of its size,” said Schulman. “We also make our underwriters available for discussions with ISOs whenever necessary. We are proud to offer competitive volume-based commissions, buyback rates and white label solutions.”
About 6th Avenue Capital, LLC
6th Avenue Capital is changing the small business financing landscape by offering a data-driven underwriting process and fast access to capital. The company employs a unique blend of industry experts and is committed to the highest operating standards, high touch merchant service, including a policy of direct merchant access to underwriters. 6th Avenue Capital is a sister company of Nexlend Capital Management, LLC, a fintech investment management firm founded in 2014 and focused on marketplace lending (consumer loans). For more information, visit www.6thavenuecapital.com.
# # #
View From The C-Suite: Alternative Funding Execs Talk Shop, The Landscape, And The Future
October 30, 2017 Alternative funders have had a roller coaster 2017 with highs and lows that will likely be remembered as a high-stakes time for the industry, one in which the rubber met the road for many and the market landscape shifted for everyone from funders, to merchants to brokers.
Alternative funders have had a roller coaster 2017 with highs and lows that will likely be remembered as a high-stakes time for the industry, one in which the rubber met the road for many and the market landscape shifted for everyone from funders, to merchants to brokers.
Three C-Suite executives in the alternative funding space — Christine Chang, CEO of 6th Avenue Capital, Heather Francis, CEO of Elevate Funding and Torrie Inouye, National Funding president — spoke with AltFinanceDaily, offering their take on some of the industry shakeups, direction of the alt lending space and upcoming developments at their respective companies.
All three execs are embracing what appears to be shaping up as a bigger and better 2018 with plans on the horizon for new products, relationships and deals but also where there could be further shakeout as the shift in the industry landscape takes hold.
Industry Landscape
6th Avenue Capital, provides short-term funding to merchants that Chang describes as “high touch, high tech and fast.” The company is building an SEC RIA compliant infrastructure as Chang believes that MCA regulation will take place over the next several years. Chang said she is sympathetic to the banks and the onerous rules that they must follow, and whatever form the industry regulation eventually takes on, the company will be ready for.

A recent story in The Wall Street Journal points to community banks comprised of those with less than $10 billion in assets historically funding local merchants in what’s dubbed character-based lending. As the name suggests, the underwriting standard for the loans was tied to the character of the business owner, which the lender knew based on personal relationships in their own communities.
The financial crisis gave rise to greater regulation, driving a spike in that model and the rest is history. Small banks were forced to direct their resources toward risk management and compliance instead of adding more personnel to service loans. The WSJ quotes a small business lender that bears repeating: “When they created too big to fail, they also created too small to succeed.”
When that door closed, however, another one opened, creating the opportunity for alt lenders to service a niche that was getting left out in the cold.
“The alternative funding industry is here to stay. That’s good news for MCA and fintech in general. There’s a need for fast funding and there will continue to be a trend toward that,” said Chang.
Banks, meanwhile, have started coming to the fintech table to compete for deals. “We’re in the process of speaking to a number of banks, some quite large and some regional, that have expressed an interest. We think this is a great opportunity for them. The idea is that we’d help them to serve a population of clients that they would not otherwise be able to serve,” said Chang.
6th Avenue has had discussions about white labeling and customizing the platform for institutions. “We would run everything for them,” said Chang.
In addition to possible new banking relationships, 6th Avenue Capital, backed by a private family and institutional investors, will expand the business model to include more investors on its platform. “We are in discussions with a number of significant international investors. It’s in the works. We’re building an institutional infrastructure, so it was always contemplated,” she said.
Elevate Funding, whose is 100% referral-based and whose product suite is comprised of a trio of MCA solutions, is coming up on its three-year anniversary in December.
“When I created Elevate, I did it with the purpose of providing a product to high-risk merchants. That’s who we deal with. We’re not dealing with credit scores. There is a level of risk to who we work with. Elevate was created to provide a product that is going to fit their needs and also provide a product that doesn’t treat them like they’re high risk. That’s who we are,” said Francis.

Gainesville, FL-based Elevate recently hired Michael Gaura to spearhead a new MCA product that the company is rolling out in 2018. Francis held the details of the new funding product close to the vest, but she did offer her views on the direction of the MCA and alternative lending space.
“I see difficulty in the coming years, especially in 2018, for qualified lead flow. You have a lot of big banks that are getting into this industry. And that’s a lot of marketing dollars that you’re competing against.”
She points to JPMorgan Chase, American Express, Square and PayPal, saying they are “huge marketing dollar companies” with tremendous access to customers on their respective platforms.
“There’s going to be a shakeout of what can you reach, who can you reach, can you get them the first time? How do you engage them to where they only want to work with you and they’re not submitting 20 applications for every website they come across?”, Francis said.
San Diego, Calif.-based National Funding is a balance sheet lender whose primary product is loans, not MCAs. The broker factor has changed significantly for the lender in a very positive way this year. “We’re really seeing sizeable growth in our broker channel in 2017 and have designed a strong and consistent process for our broker clients” Inouye said. The leads have been driven by a variety of factors, not the least of which comes down to CAN Capital and Bizfi’s loss being National Funding’s gain.

“That’s a factor we can’t ignore. The broker community has rewarded us for being consistent and building those relationships and being a partner to them,” Inouye said. “We definitely saw an uptick in business when they left the space. I can say we’ve continually experienced sizeable growth in our broker channel year over year but 2017 was beyond what we had expected. It surpassed other years.”
Incidentally, National Funding was one of the earliest alt funders on the scene along with CAN Capital in the 1990s. CAN’s fate started unraveling about this time a year ago.
“It’s not positive when you see that happen in the industry. However, we are really focused on what we’re doing and the decisions we’re making internally. I think that’s why we’ve consistently had profitable growth over the years. We’ve stayed true to our underwriting principles and the market seems to have rewarded us. We were consistent and not erratic. Brokers know they can rely on us and feel confident that we would quickly fund their deal once we issued an approval,” said Inouye.
The Broker Effect
Elevate, a balance sheet funder, relies on outside brokers and referrals for deals. “I don’t find it a disadvantage for us not having an internal sales team. A lot of companies in this space have the ability for a chief marketing officer who focuses entirely on leads. Elevate isn’t there yet. Will we be there in five years? Maybe. Marketing can change by that time,” Francis said.
6th Avenue Capital welcomes relationships with brokers as well. “We have an in-house business development team that works with brokers. 6th Avenue Capital is also considering direct sales in niche strategies in its future,” said Chang.
6th Avenue Capital has a starter program in which there are no guarantees but considers businesses that have been in existence for less than a year and businesses with credit scores of 500 or more. Plus, they’re willing to do consolidations up to two advances.
In addition, 6th Avenue Capital is open to offering financing to brokers. “It’s really good in that there is an alignment of interests and allows brokers to participate in the deals they put forth. If they think the merchant is credit worthy and a terrific opportunity, they participate. Everyone has skin in the game and interests are aligned,” Chang said.
Technology
While technology is at the core of fintech, all three of the companies take a hybrid approach when it comes to credit underwriting comprised of a tech platform and the human touch, which perhaps keeps character-based lending alive in some form.
With respect to fintech, “6th Avenue Capital’s philosophy is that technology is a tool to supplement human underwriting. We use technology to detect fraud, manage workload processes and manage risk. We do not use technology to make our final decisions,” said Chang.
Specifically, 6th Avenue Capital benefits from research, artificial intelligence and predictive technology of its sister company Nexlend Capital. 6th Avenue Capital has customized Nexlend’s consumer lending algorithmic intellectual property, which uses machine learning and credit analysis with high speed execution to make better and faster decisions.
Elevate also takes a dual-approach to its underwriting process. “I believe in a hybrid method. You have to have someone looking at it, to have eyes on the paper at some point in the process. This doesn’t mean a computer system can’t help to weed out what might not meet the criteria, but I do believe there needs to be a person reviewing the files,” Francis said.
National Funding was started as an equipment leasing company. “We apply some principles we learned as a leasing company and take into account all of the attributes that go into that business in addition to FICO and cash flow,” Inouye said.
Automation is an area of technology that they continue to look to for innovation and process efficiencies. “We do serve our customers online, but we also provide a human contact as well. We deliver a loan experience that builds trust and confidence with customers. We try to deliver on what our customers want in the most efficient way,” said National Funding’s Inouye.
National Funding continues to look at construction deals and accepts them as a niche in their portfolio, which Inouye said differentiates the company. “It allows us to be more flexible and comfortable with certain industries that other lenders might stay away from.”
Corporate Culture
2017 has been a roller coaster year for fintech including alt funders. While there have been plenty of bright spots, there was also some fallout that left veteran players scrambling to salvage either their reputation, status as a funder or both.
SoFi has been at the center of controversies that resulted in the Mike Cagney leaving his chairman post with plans to step down as CEO. Most recently, the lender has removed its application for a bank charter, according to reports.
We asked Elevate’s Francis about it. “SoFi is a very big company. They’re to the level where the CEO has people to answer to. They have a checks and balances system they need to go through,” said Francis. “It worked, and they removed him.”
Francis maintains an open-door policy with her employees, and she says all you can do is focus on your house and keep your house in order. “My door is always open. That’s our office policy. They use that quite frequently; it’s a catch 22,” she said with a laugh.
Fintech and Diversity
Something else that all three executives have in common is that they are all women in top roles in fintech, an industry that isn’t known for its diversity.
6th Avenue’s Chang’s career includes working at a large institutional bank for six years. Out of 200 professionals, only four of them in her group were women. “At the end of the day, performance is the best differentiator. If you perform well, it presents unique opportunities. At 6th Avenue Capital, diversity is embraced. Our underlying merchants aren’t just one gender or color. Diversity helps us understand the needs of small businesses better, so we can provide fast and customized funding quickly,” she said.
Q&A With Noah Breslow On Replacing ACH For Realtime Funding and More
October 25, 2017 An announcement by OnDeck, Ingo Money and Visa this week at Money2020 may be more consequential than it appeared. That’s because the partnership enables OnDeck to actually fund a merchant’s bank account (not their debit card) on days, nights, weekends, and holidays. Such a feature is not possible in the realm of ACH where funding typically takes place on the next business day and only if the transaction is submitted before a predetermined cutoff time. AltFinanceDaily got to learn more about how this works in an interview with OnDeck CEO Noah Breslow on Tuesday as well as the opportunity to pick his brain about a few other things. Below is a curated excerpt of the interview that has been edited for brevity.
An announcement by OnDeck, Ingo Money and Visa this week at Money2020 may be more consequential than it appeared. That’s because the partnership enables OnDeck to actually fund a merchant’s bank account (not their debit card) on days, nights, weekends, and holidays. Such a feature is not possible in the realm of ACH where funding typically takes place on the next business day and only if the transaction is submitted before a predetermined cutoff time. AltFinanceDaily got to learn more about how this works in an interview with OnDeck CEO Noah Breslow on Tuesday as well as the opportunity to pick his brain about a few other things. Below is a curated excerpt of the interview that has been edited for brevity.
AltFinanceDaily: For this real time funding you announced, do you have to have a Visa debit card?
Breslow: You do not, but you have to have a debit card. 70% of small business owners have debit cards. And this will work with Visa or Mastercard.
AltFinanceDaily: So you’re not actually funding a merchant’s debit card, you’re funding their bank account but using the Visa network as the mechanism?
Breslow: It’s the rails, it’s the way to get the money into a small business owner’s checking account. My prediction is that every funder in the industry is going to be doing this in a couple of years. It’s going to be faster and small businesses will start to expect it. Now instead of waiting 2 days to get the money into someone’s account, it can be done on nights, weekends, holidays, 365 days a year.
AltFinanceDaily: So you can fund a merchant’s bank account on the weekend?
Breslow: Yes, it’s real time. And to be clear we partnered with Ingo Money, Visa has the rails. Ingo is our interface point, they do the PCI compliance and the rest. We looked at a bunch of different players in the market and Ingo was unique in that they had covered small business checking accounts. Some of this stuff is happening in consumer already. We’re the first lender to use these rails for either consumer or small business in the US.
AltFinanceDaily: Has this already gone into effect?
Breslow: No, it’s coming out in a couple months. Early 2018.
AltFinanceDaily: Does this system work with every bank already?
Breslow: It doesn’t work with every bank yet. It works with most of them, all of the major ones.
AltFinanceDaily: Speaking of payments… Square. PayPal. They’re both payments companies first that went into lending. Is there a potential reverse play for OnDeck to go into payments?
Breslow: Right now our product expansion stuff is very focused on additional lending products. I still feel like we haven’t lived up to our full potential there. There’s a couple other product categories that we’ve looked at and thought about. Equipment finance is one, invoice factoring, small business credit cards. And so we look to be the best small business lender in the world with the best set of products. And then we can partner with a lot of the payments companies. But right now, no we’re not going to sell merchant processing. Never say never, but not in the near future.
AltFinanceDaily: Any news on the Chase front?
Breslow: We re-upped our agreement with them in early August. The customer experience is amazing, our platform is scaling, and we’re making progress. I can’t tell you a lot of other details about it.
AltFinanceDaily: I’ve heard from folks in the industry about merchants who are being debited by Chase either daily or weekly. Is that you?
Breslow: That would be our platform. Chase’s product is more or less like the OnDeck product but cheaper obviously. It’s a daily or weekly collected loan. It goes up to 24 months for $200,000.
AltFinanceDaily: I want to ask you about brokers, or as you call them “funding advisors.” Do you anticipate reliance on them increasing or decreasing?
Breslow: Stable. I don’t anticipate it moving up or down. We really like the funding advisors that we have and we’re continuing to grow with them. We’re also adding some new ones.
AltFinanceDaily: What makes a good broker? What can they do to do things right?
Breslow: The value equation between the merchant, the lender and yourself has to be in balance. They should also be efficient and know the credit box of the lender they’re working with. They should invest in their employees, train them, and they should become more sophisticated about their online marketing and CRMs, which we’ve been seeing.
AltFinanceDaily: Everyone’s talking about blockchain at this conference. Is there a way that blockchain fits into online lending and possibly OnDeck?
Breslow: I love the technology, I’m very intrigued by it. But we’re not actively using it and it’s not like I have a secret blockchain project in the works.
AltFinanceDaily: Is there a universe in which OnDeck considers making an acquisition of a company?
Breslow: So we’re not totally opposed to that. They’re might be an opportunity for a complementary product or a complementary team. I think you’re going to see a lot of consolidation in the industry in the next 3-5 years.
The Top Small Business Funders By Revenue
October 23, 2017The below chart ranks several companies in the non-bank small business financing space by revenue over the last 5 years. The data is primarily drawn from reports submitted to the Inc. 5000 list, public earnings statements, or published media reports. It is not comprehensive. Companies for which no data is publicly available are excluded.
| Company | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 |
| Square1 | $1,708,721,000 | $1,267,118,000 | $850,192,000 | $552,433,000 | $203,449,000 |
| OnDeck2 | $291,300,000 | $254,700,000 | $158,100,000 | $65,200,000 | $25,600,000 |
| Kabbage3 | $171,784,000 | $97,461,712 | $40,193,000 | ||
| Swift Capital4 | $88,600,000 | $51,400,000 | $27,540,900 | $11,703,500 | |
| National Funding | $75,693,096 | $59,075,878 | $39,048,959 | $26,707,000 | $18,643,813 |
| Reliant Funding5 | $51,946,472 | $11,294,044 | $9,723,924 | $5,968,009 | $2,096,324 |
| Fora Financial6 | $41,590,720 | $33,974,000 | $26,932,581 | $18,418,300 | |
| Forward Financing | $28,305,078 | ||||
| Gibraltar Business Capital | $15,984,688 | ||||
| Tax Guard | $9,886,365 | $8,197,755 | $5,142,739 | $4,354,787 | |
| United Capital Source | $8,465,260 | $3,917,193 | |||
| Blue Bridge Financial | $6,569,714 | $5,470,564 | |||
| Lighter Capital | $6,364,417 | $4,364,907 | |||
| Fast Capital 360 | $6,264,924 | ||||
| US Business Funding | $5,794,936 | ||||
| Cashbloom | $5,404,123 | $4,804,112 | $3,941,819 | $3,823,893 | $2,555,140 |
| Fund&Grow | $4,082,130 | ||||
| Nav | $2,663,344 | ||||
| Priority Funding Solutions | $2,599,931 | ||||
| StreetShares | $647,119 | $239,593 | |||
| CAN Capital7 | $213,402,616 | $269,852,762 | $215,503,978 | $151,606,959 | |
| Bizfi8 | $79,886,000 | $51,475,000 | $38,715,312 | ||
| Quick Bridge Funding | $48,856,909 | $44,603,626 | |||
| Funding Circle Holdings9 | $39,411,279 | $20,100,000 | $8,100,000 | ||
| Capify10 | $37,860,596 | $41,119,291 | |||
| Credibly11 | $26,265,198 | $14,603,213 | $7,013,359 | ||
| Envision Capital Group | $21,034,113 | $19,432,205 | $12,071,976 | $11,173,853 | |
| Capital Advance Solutions | $4,856,377 | ||||
| Channel Partners Capital | $2,207,927 | $4,013,608 | $3,673,990 | $2,208,488 | |
| Bankers Healthcare Group | $93,825,129 | $61,332,289 | |||
| Strada Capital | $8,765,600 | ||||
| Direct Capital | $432,780,164 | $329,350,716 | |||
| Snap Advances | $21,946,000 | ||||
| American Finance Solutions12 | $5,871,832 | $6,359,078 | |||
| The Business Backer13 | $19,593,171 | $11,205,755 | $9,615,062 |
1Square (SQ) went public in 2015
2OnDeck (ONDK) went public in 2014
3Kabbage received a $1.25B+ private market valuation in August 2017
4Swift Capital was acquired by PayPal (PYPL) in August 2017
5Reliant Funding was acquired by a PE firm in 2014
6Fora Financial was acquired by a PE firm in 2015
7CAN Capital ceased funding operations in December 2016 but resumed in July 2017
8Bizfi wound down in 2017. Credibly secured the servicing rights of their portfolio
9Funding Circle’s primary market is the UK
10Capify’s US operations were wound down in early 2017 and their operations were integrated with Strategic Funding Source. Capify’s international companies are still operating
11Credibly received a significant equity investment from a PE firm in 2015
12American Finance Solutions was acquired by Rapid Capital Funding in 2014, who was then immediately acquired by North American Bancard
13The Business Backer was acquired by Enova (ENVA) in 2015
The Voice of Main Street – Small Businesses Share Their Experience With Non-bank Finance
October 18, 2017
If she hadn’t scored the $250,000 loan through Breakout Capital in 2015, Jackie Luo says, the commercial-software firm she heads in Baltimore could not have made the “strategic hires” and purchased the new server to support additional customers and maintain the company’s 30% growth rate.
“Without that infusion of capital” from the McLean (Va.)-based lender, says Luo, chief executive at E-ISG Asset Intelligence, the software solutions provider would have been hard-pressed to deploy the “bandwidth and capacity” necessary to meet burgeoning demand.
And demand there is. Luo says billing for her company’s services helping more than 100 businesses and government agencies improve operational efficiency by keeping tabs on multiple assets — human, financial and equipment — topped $1.5 million last year, up from $1 million in 2015. This year, moreover, E-ISG is on track to collect nearly $2 million.
Meantime, she says, the $250,000, 10-year note at 6% interest she obtained with the help of Breakout was both a good deal and convenient: she reports securing the financing in three weeks, compared with the six months that a commercial bank would likely have taken. In addition, she’s been able to forge a better relationship with Breakout than with a faceless financial institution.
“We are a small business,” she says, “and we’d be just one in a million at a big bank like Wells Fargo. They wouldn’t give us much attention.” With Breakout, Luo adds: “I have the freedom to make decisions about infrastructure investments without worrying about the short-term. And I don’t have to deal with people second-guessing me.”
Had she not gotten the financing, moreover, “I would not be able to pay myself,” she says. “I’d have to use my salary as working capital.”
Luo is not alone. Her company’s story of finding much-needed capital from a nonbank financial company is increasingly common. It has always been challenging for small businesses to obtain credit from a big bank — roughly a financial institution larger than $10 billion in assets. But the small and community banks that have been the lifeblood for small businesses have also been winding down their small-business lending as well, according to a March, 2016, working paper published by the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia.
“As recently as 1997, small banks, with less than $10 billion in assets, accounted for 77% of the small business lending market share issued by commercial banks,” co-authors Julapa Jagtiani and Catharine Lemieux write in “Small Business Lending: Challenges and Opportunities for Community Banks.” However, the market share dropped to 43% in 2015 for small business loans with origination amounts less than $1 million held by depository institutions.
“The decline is even more severe for small business loans of less than $100,000,” they add, “where the market share for small banks under $10 billion declined from 82% in 1997 to only 29% in 2015.”
 The Philadelphia Fed study notes that alternative nonbank lenders are filling a widening gap. “By using technology and unconventional underwriting techniques, many alternative lenders are competing for borrowers with offers of faster processing times, automatic applications, minimal demands for financial documents, and funding as soon as the same day.” And the Fed study finds that it’s likely that nonbank lenders, which are growing rapidly, are having a positive effect by “increasing the availability of credit, particularly to newer businesses that do not have the credit history required by traditional lenders.”
The Philadelphia Fed study notes that alternative nonbank lenders are filling a widening gap. “By using technology and unconventional underwriting techniques, many alternative lenders are competing for borrowers with offers of faster processing times, automatic applications, minimal demands for financial documents, and funding as soon as the same day.” And the Fed study finds that it’s likely that nonbank lenders, which are growing rapidly, are having a positive effect by “increasing the availability of credit, particularly to newer businesses that do not have the credit history required by traditional lenders.”
Meantime, the Small Business Administration reports that small businesses remain essential to the health of the U.S. economy. Businesses with fewer than 500 employees account for 55% of overall employment in the U.S., according to the agency, and are responsible for creating two out of every three net new jobs. Which means that alternative funding sources — which do not, it is worth noting, depend on depositors’ money, as banks do — are playing an increasingly important and largely unrecognized role in the country’s economic fortunes, notes Cornelius Hurley, a law professor at Boston University and executive director of the Online Lending Policy Institute. “They’re still a small percentage of the overall lending picture,” he says of nonbank financial companies, “but they’re an emerging force and a lot of small businesspeople certainly depend on them. If they disappeared tomorrow,” he adds, “a lot of businesses would be wiped out too.”
To find out what is happening in the real world, AltFinanceDaily interviewed small business owners around the country: among others, a Houston sports medicine provider, a Connecticut restaurateur, a Midwestern truck hauler, and a Maryland hardware-store owner. Some recounted being shunned by banks because of poor credit while others registered unhappiness with traditional financial institutions as inconvenient and impersonal. While some who turned to alternative lenders admitted they would have preferred not to be paying dearly for borrowing or for cash advances, most said the tradeoff was worth it.
The existence of alternative lenders has made it possible for these businesspeople to meet payrolls, pay contractors and suppliers even when business was slow or billings stalled. Customers with alternative funders – in addition to Breakout’s customers, AltFinanceDaily spoke to clients of Pearl Capital Business Funding and Merchants Advance Network– also reported that they were able to purchase or replace equipment and maintain inventory, hire additional employees and accept new customers, pay for upkeep and upgrades of their business’s physical plant, and make other expenditures necessary to keep operations up-and-running.
Jason, for example, who heads a family business in Louisiana manufacturing and selling pesticides (and who asked to be identified only by his first name), reports that his suppliers began demanding that he pay in advance for chemical feedstock after he took a “financial hit following a nasty divorce.”
The roughly $1 million (annual sales) business — which was started by his parents back in 1960 — furnishes chemicals mainly to cotton farmers and homeowners in Louisiana and Texas, most of whom purchase the company’s products through feed and hardware stores. Jason says he spends a substantial amount of time on the road handling sales and distribution.
 His suppliers not only require him to pay for the chemicals upfront but, following his divorce, they now insist upon larger purchases as well. Following the departure of a previous lender, he says, Breakout stepped in with an $80,000, 12-month loan in March, 2016, which he was able to repay within six months. This was followed by a $60,000 borrowing in March, 2017, which he again paid down early – in 90 days, Jason says – and the account manager at Breakout “went to bat for me and gave me an additional discount for early payment.”
His suppliers not only require him to pay for the chemicals upfront but, following his divorce, they now insist upon larger purchases as well. Following the departure of a previous lender, he says, Breakout stepped in with an $80,000, 12-month loan in March, 2016, which he was able to repay within six months. This was followed by a $60,000 borrowing in March, 2017, which he again paid down early – in 90 days, Jason says – and the account manager at Breakout “went to bat for me and gave me an additional discount for early payment.”
Had Breakout not provided external funding, Jason says, he would have been “wiped out.” He adds with feeling: “It would have meant the end of me.” And sinking the fortunes of the company would also have spelled job losses for five employees, including both his son, who works part-time, and his sister, the business’s co-manager. “Now I’m out of the hole,” he says.
In Houston, Anna, co-owner of a physical therapy and sports medicine concern, was interviewed in August just before Hurricane Harvey loomed on the horizon. “We’d been around for four years and growing rapidly,” she says, asking to be identified only by her first name, and “we couldn’t keep up with the growth.”
Anna recalls that a few years ago (she is vague about the exact dates) the company needed $50,000 to $60,000 to add equipment and staff to meet the growing demand. Because of some “ups and downs” in her business and credit history, however, a bank loan was out of the question. “My credit wasn’t the best,” Anna says, “and we had not been in business the five-to-seven years that most banks want.” She began casting about for financing and quickly saw that factoring would not be a suitable choice for a business like hers, which depends heavily on third-party payments from health insurance providers. “Companies using factoring are taking money based on credit card payments,” she says, “and we’re not a restaurant or a bar. So we can’t pay a percentage of every transaction.” Typically, she notes, getting paid by an insurance company involves a “90-day turnaround.”
 Anna went online, did some research, and talked to three or four nonbank lenders searching for the “right kind of company.” That led her to Breakout. “What I really liked about them is that they did a lot of due diligence on our field,” she says. “They did their homework, asking us: ‘What are your collections and payroll? How much outstanding debt do you have?’ They also asked to see our actual bank statements.”
Anna went online, did some research, and talked to three or four nonbank lenders searching for the “right kind of company.” That led her to Breakout. “What I really liked about them is that they did a lot of due diligence on our field,” she says. “They did their homework, asking us: ‘What are your collections and payroll? How much outstanding debt do you have?’ They also asked to see our actual bank statements.”
Despite the high level of due diligence that Breakout performed, Anna says, it only took “maybe three or four days” for the loan to be approved and for the money to land in her bank account. Before long, she was off to the races. With the added capital, she hired three more employees – bringing the employee headcount to 18 — purchased more gym equipment, made payroll, and paid off miscellaneous expenses.
The added capacity and fortified staff, meanwhile, enabled the company to “almost triple its volume,” the entrepreneur says. And not only did the financing “put me in a good financial place,” Anna adds, but after repayment, Breakout made it possible for her to effect a merger with a competitor by approving a second loan for about $30,000. “The best thing about Breakout,” she says, “has been the communication. One time I did need to make a payment two or three days late. But I just called (the account manager). I was very surprised because these kinds of companies are seen as a last resort. But it was like they were investing in us.”
John Speelman, who owns Poolesville Hardware in Poolesville, Md., can boast a raft of five-star Yelp reviews online. “Extremely helpful and friendly service, surprisingly good selection (and) the complete opposite of a big box hardware chain,” raves one customer. “It is so rare to find a well-stocked store that has helpful personnel—makes this store a real gem!” says another fan.
For his part, Speelman attributes much of his hardware store’s popularity to the financing arrangement that he’s been able to work out over the past eight years with Merchants Advance Network, a Fort Lauderdale (Fla.)-based alternative funder. “It takes money to make money,” is one of his pet aphorisms.
Located roughly 35 miles west of the White House, the hardware store boasts a clientele who tend to arrive in BMW’s rather than the pickup trucks that predominated a decade or so ago in this exurban community of some 5,000 denizens. Whatever their class background, though, they’re looking for items that are not a good match for an online purchase. “People don’t buy a toilet plunger, a can of paint or picture-hanging stuff online,” Speelman says. “Because they want to do that today,” he says, “they won’t order with Amazon.”
“One industry that has not been impacted” by online merchandisers, he adds, “is the garden center. They’ll buy a garden hose, weed killer and seeding,” he explains of his regular customers. “And light bulbs” while they’re there, he adds. “We’re like the 7-Eleven — a convenience store.”
To guarantee that convenience, Speelman pays cash-in-advance for most of his inventory, and banks have not been helpful. He contrasts the relationship he has with Michael Scalise, the chief executive at Merchants Advance, with loan officers at commercial banks. “It’s hard to get a loan for anything in retail,” he says. Never mind that he maintains “a high credit rating and I never bounce a check,” he went on. “There are no more local banks. At M&T Bank, all the managers I knew are gone and there’s always a new teller. The banking industry is a revolving door.” So he opts for capital from Merchants Advance “when I need 30-40-50 grand in a day, I use Mike’s money” even though the cost can be as steep as 25%, he says. If he doesn’t have something in stock – specialty items like ammo boxes, a Sugarplum tent, as many as 32 packs of size D batteries, metric measuring tapes – he can put in a special order with suppliers. But he prides himself on the full panoply of wares on his shelves. “You can’t sell from an empty cart,” is another of his favorite sayings.
Lori Hitchcock, who also draws capital from Merchants Advance, is manifestly displeased with the banking industry. She’s an owner with her husband of Hitchcock Trucking, the couple’s 60-year-old family business, which is located on a ten-acre tract in Webberville, Mich., situated between Detroit and Lansing, the state capital.
Of her experience with banks, Hitchcock says: “At the time we went with (Merchants Advance), banks weren’t lending. And they’re still not lending. We’re considered high-maintenance and high-risk. Banks don’t want a bunch of trucks” should they foreclose on a loan, she observes. “If you’re a farmer, they can take all your land. Great! In this crazy world you live in, it’s hard to get the banks interested.”
 The Hitchcock family’s fleet of ten Peterbilt semis hitch up to more than 20 trailers and truck bodies – flatbeds, dump trucks, vans, and refrigerated trucks or “reefers” – and haul grain, sweet corn, onions, celery, fertilizer, and soft drinks across the Midwest. Most recently, she says, the family business took out $80,000 from Merchants Advance to expand its fleet and buy another reefer trailer and a backhoe. “Out here in the country, you always need a backhoe,” she says.
The Hitchcock family’s fleet of ten Peterbilt semis hitch up to more than 20 trailers and truck bodies – flatbeds, dump trucks, vans, and refrigerated trucks or “reefers” – and haul grain, sweet corn, onions, celery, fertilizer, and soft drinks across the Midwest. Most recently, she says, the family business took out $80,000 from Merchants Advance to expand its fleet and buy another reefer trailer and a backhoe. “Out here in the country, you always need a backhoe,” she says.
To satisfy her lender, the company makes daily ACH payments. “I’m not going to lie and say that things aren’t tight,” she says. “It is a burden. You just have to have constant cash-flow – which we do have. And it’s important to have good relationships…I can usually tell three weeks in advance if (making payments) is going to be challenging. So it all comes down to being loyal to people.”
Whatever the struggle to keep up with debt payments, it beats using her own money. “My husband and I are raising a family,” Hitchcock says, “and it’s nice having the cash so you’re not putting your personal earnings into the company.”
In Manchester, Conn., a stone’s throw east of Hartford, Corey Wry says that he wouldn’t be able to operate his two, highly rated restaurants just off Interstate 84 – Corey’s Catsup & Mustard and Pastrami on Wry – if he didn’t have funding from Pearl Capital, a New York (N.Y.)-based alternative funding company. A graduate of Johnson & Wales University in Providence, a restaurant-and hotel school, Wry describes himself as “a culinary guy” whose first love is serving food that’s both innovatively prepared and delicious. He candidly admits that his credit hit “rock bottom” after a confluence of untoward events.
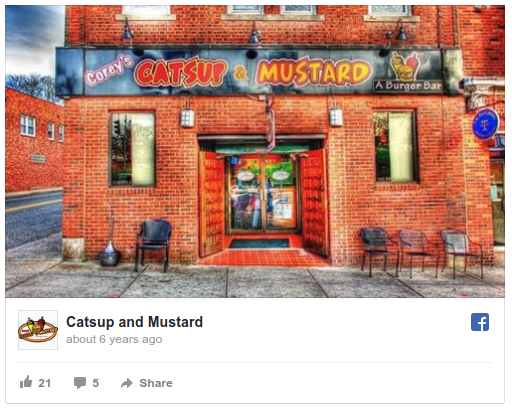
Last year, a third restaurant in town, Chops & Catch, that he and some partners had “bootstrapped” had to shut down after six years of operation. Despite generally favorable reviews for such creative fare as the “lobsterburger,” the surf-and-turf themed restaurant was a money-loser. He was also struggling to pay off credit cards. And he’d been late more than once on car payments.
At the same time, Wry was in the process of moving Pastrami & Wry — a deli whose moniker is wordplay on his last name – to a new location. Both the general contractor and electrician were “over-budget” on that project, he says. Meanwhile, Catsup and Mustard, a hamburger spot, needed to be spruced up. Says he: “It was getting busier and the original seats were worn. I had a hole in a booth big enough to swallow someone.”
He approached a few banks for a loan and “it did not seem like it was going to happen,” he says. “Then I got a cold call from one of these financiers. Some of them had super-high rates. When you have bad credit but need to make capital improvements you do what you have to do.”
He’s accessed more than $100,000 from several alternative funding sources, including Pearl – from which he reports getting merchant cash advances for $30,000. But hard as it is to meet the obligations, which typically require a daily ACH payment, the financing has made renovating the burger place possible. Moreover, he’d still be on the hook with plumbers and other contractors – all of whom are local tradesmen and would likely be paying him personal visits until they were repaid — for the relocation of Pastrami & Wry.
“Business is good,” says Wry, who at 40 is single, often works 15-hour days, and says that he doesn’t have time for a girlfriend, much less a wife and family. “I’ve still got $3,200 on the books with the electrician,” he adds, “which means that I won’t be able to purchase a deli slicer. I have to plan these things out…”
James McGehee, a partner at the boutique accounting and tax-preparation firm McGehee, Davis & Associates, which is located in the Denver suburb of White Ridge, reports that the firm took a merchant cash advance from Pearl Capital, among other financiers, to bridge the gap between tax season and the rest of the year when billings invariably diminish. “Our overhead is pretty high,” he explains. “We’ve added two employees. We’ve been expanding on what we were doing, adding tax and accounting clients.”
A very conservative, sober-sounding man, McGehee explained that his credit was nonetheless “trashed” after he suffered from health problems five years ago. “Major stuff,” he says, “it was open-heart surgery.” The medical ordeal meant that he could not work for a time and had trouble paying his bills. “Some family members helped me through the mortgage and utilities payments and I ended up in arrears and in credit card debt,” he says.
All of which made an alternative source of financing his firm’s only option. “I’m not sure how we heard about Pearl,” he says. “I think they just happened to call. We took out [$11,000]. It was not a huge amount. We also borrowed $9,000 from another entity. We paid it all back during tax season. The terms were pretty steep,” McGehee adds.
“But when you need the money for cash-flow,” he explains, “you just absorb it. You grin and bear it. When you need the money, you need the money.”
Platinum Rapid Funding Group Hires Dynamic New CFO
October 16, 2017 Uniondale, NY: Michael Kennedy, former CFO of BizFi, Mastercard Europe, and American Express Latin America, has joined Platinum Rapid Funding Group LLC. As CFO, Michael is a highly accomplished professional with over thirty years of industry experience, most recently serving as an effective strategist and visionary at BizFi.
Uniondale, NY: Michael Kennedy, former CFO of BizFi, Mastercard Europe, and American Express Latin America, has joined Platinum Rapid Funding Group LLC. As CFO, Michael is a highly accomplished professional with over thirty years of industry experience, most recently serving as an effective strategist and visionary at BizFi.
Ali Mayar commented “we are so pleased to announce that Michael is officially on board, and we’re excited to continue on this road of growth and prosperity, now aided by his industry expertise. We view his appointment as a sign of our commitment to being the leading company in our industry.”
Michael Kennedy enthusiastically stated “I am thrilled to join Platinum Rapid Funding at this exciting time in the Company’s evolution. As their CFO, I am impressed with the strong foundation that Ali and his team have built and I look forward to helping them to bigger and better things.”
About Platinum Rapid Funding Group
Platinum Rapid Funding Group is a Merchant Cash Advance company that provides working capital to businesses nationwide. Founded in 2012, Platinum’s mission is to help businesses succeed by providing service to merchants seeking rapid alternative financing. Platinum has seen exponential growth by utilizing a unique business model, harnessing manpower, technology and proprietary data, placing them at the top of the industry standard.