SCORCHED EARTH – Controversial Bill Could Eliminate Marketplace Lending, Merchant Cash Advance and Nonbank Business Loans in Illinois (and starve small businesses in the process)
April 9, 2016
The State of Illinois wants to make it a Class A misdemeanor for providing small businesses with quick, easy working capital.
The world’s strangest bill, dubbed the Small Business Lending Act, could send marketplace lenders, nonbanks, and merchant cash advance companies to prison for up to 1 year if applicants don’t submit at the very least, their most recent six months bank statements, the previous year’s tax return, a current P&L, a current balance sheet, and an accounts receivable aging.
Loans in which the monthly payments exceed at least 50% of the business’s monthly net income would be illegal, which implies that any business that is either breaking even or running at a loss would be banned from obtaining a loan from alternative sources.
This is not an April Fools’ prank. Not even preemption granted under the National Bank Act or Federal Deposit Insurance Act is safe.
Introduced into the State Senate under the pretense that it would squash predatory lenders, the bill’s licensing and compliance proposal would also effectively outlaw marketplace lending and securitizations by making the sale of loans illegal unless it’s to a bank or another state-licensed party. Even merchant cash advances are referenced specifically but almost as an afterthought and defined in such a way that even traditional factoring companies may be in jeopardy.
No licensee or other person shall pledge, assign, hypothecate, or sell a small business loan entered into under this Act by a borrower except to another licensee under this Act, a licensee under the Sales Finance Agency Act, a bank, savings bank, community development financial institution, savings and loan association, or credit union created under the laws of this State or the United States, or to other persons or entities authorized by the Secretary in writing. Sales of such small business loans by licensees under this Act or other persons shall be made by agreement in writing and shall authorize the Secretary to examine the loan documents so hypothecated, pledged, or sold.
 At a time when most fintech lenders are advocating for smart regulation, the State of Illinois apparently wants to end all nonbank commercial finance under $250,000 completely, with the exception of one organization (which we’ll get to shortly).
At a time when most fintech lenders are advocating for smart regulation, the State of Illinois apparently wants to end all nonbank commercial finance under $250,000 completely, with the exception of one organization (which we’ll get to shortly).
There are some exemptions granted under this proposal of course. Loans over $250,000 aren’t subject to it, nor are any loans made by Illinois-based banks or credit unions, that is unless they are acting as the agent for another party like say perhaps a marketplace lender.
Hidden inside is also an exemption for nonprofit lenders, a loophole left open for Accion Chicago, the nonprofit masterminds behind the bill who seem to want the entire state’s lending market all for themselves.
Illinois State Senator Jacqueline Collins Introduced This Bill
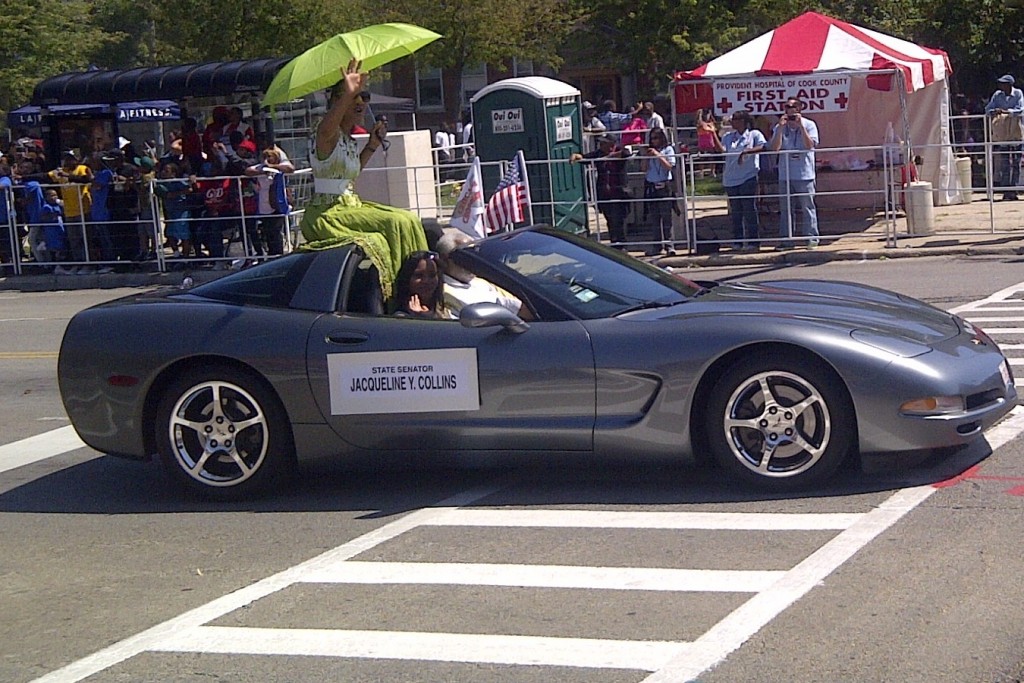

Senator Collins introduced the legislation as an amendment to Senate Bill 2865 on April 6th. A former journalist, she’s now the chairwoman of the Illinois Senate Financial Institutions Committee. Among her self-professed accolades is that she “has played a key role in addressing predatory lending and high foreclosure rates in Chicago through legislation that protects homebuyers and homeowners with subprime mortgages.” She lists the Mortgage Rescue Fraud Act, the landmark Sudan Divestment Act and the Payday Loan Reform Act among her major legislative accomplishments.
It’s no surprise then that sections of the bill are borrowed straight out of the Payday Loan Reform Act. Collins isn’t acting on her own however…
Chicago City Treasurer Kurt Summers
In January, Senator Collins joined Chicago City Treasurer Kurt Summers in a call for “new legislation to protect small business owners from misleading and dishonest predatory lenders.” In a closed-door hearing, the committee supposedly heard from business owners, advocates and elected officials on predatory lending.
“Chicago’s small business community deserves protection from the unchecked greed of predatory lenders,” Treasurer Summers said. “While access to capital is the number one concern of small business owners across the state, bank and commercial loans continue to decline, steering them to underhanded lenders. As we continue to urge banking partners to increase their local investment, this new, common-sense legislation would ensure transparency in lending that so often puts our entrepreneurs at risk.”
Of note is his use of the phrase “banking partners” since this bill has bankers all over it, as we’ll get into shortly. Summers represents the Chicago Mayor’s office and the Mayor’s office says they’ve launched this campaign thanks to partners like Accion Chicago.
Hon. Kurt Summers, Treasurer, City of Chicago from City Club of Chicago on Vimeo.
Accion Chicago and the Mayor’s Office
Last year, Mayor Rahm Emanuel announced a joint campaign with Accion Chicago to help small businesses avoid predatory lending.
Accion Chicago, ironically makes business loans themselves, having originated 535 loans totaling $4.8 million in 2014 with a maximum loan size of $100,000.
Who is Accion Chicago really?
The Small Business Lending Act virtually ensures that small business loans under $250,000 only be facilitated by banks and nonprofits. Isn’t it convenient then that Accion Chicago is not only a nonprofit, but also funded and staffed by banks?
According to their 2014 annual report, Citibank and JPMorgan Chase were two of their three largest supporters (the third was the US Treasury!). Below are some of the figures:
$100,000+
- Citibank
- JPMorgan Chase
$50,000 – $99,999
- Bank of America
$20,000 – $49,999
- Fifth Third Bank
- PNC Bank
- U.S. Bank
$5,000 – $19,999
- American Chartered Bank
- Alliant Credit Union
- BMO Harris Bank
- First Bank of Highland Park
- First Eagle Bank
- First Midwest Bank
- Ridgestone Bank
- State Bank of India
- The PrivateBank
- Wells Fargo Bank
About a dozen more banks gave less than $5,000.
 JPMorgan Chase has also been a partner of the annual Taste of Accion fundraising event, and was the lead sponsor in 2014, a spot that costs $30,000. Benefactor sponsorships which cost $20,000 each were comprised of American Chartered Bank, Capital One, Northern Trust Company, and Wintrust Bank. And the lesser sponsorships? Again, mostly banks.
JPMorgan Chase has also been a partner of the annual Taste of Accion fundraising event, and was the lead sponsor in 2014, a spot that costs $30,000. Benefactor sponsorships which cost $20,000 each were comprised of American Chartered Bank, Capital One, Northern Trust Company, and Wintrust Bank. And the lesser sponsorships? Again, mostly banks.
You know who hasn’t donated to Accion Chicago? Marketplace lenders and merchant cash advance companies.
Accion Chicago raised only $1.4 million in 2014 from public support, the bulk of which came from banks or related traditional financial institutions. So is it just a coincidence that this predatory lending bill they’re supporting grants exemptions to all the banks from compliance?
Accion Chicago’s 2014 Board of Directors includes executives from:
- American Chartered Bank (chairman)
- First Eagle Bank
- JPMorgan Chase
- Ridgestone Bank
- MB Financial Bank
- Talmer Bank & trust
- Citibank
- First Midwest Bank
The 2014 committees were made up almost entirely of bank executives from:
- First Eagle Bank
- The PrivateBank
- Ridgestone Bank
- U.S. Bank
- JPMorgan Chase
- Forest Park National Bank & Trust Co.
- MB Financial Bank
- FirstMerit Bank
- Wintrust Bank
- Standard Bank & Trust Co.
- First Midwest Bank
- Wells Fargo Bank
- Seaway Bank & Trust Co.
- Metropolitan Capital Bank
- Evergreen Bank Group
- First Financial Bank
- PNC Bank
Thanks to the impartial work of these good citizens, they have discovered that small businesses should only be working with banks or nonprofits funded and staffed by banks and have craftily devised a bill to legislate all the alternatives out of existence.
If this was really about predatory lending, then they screwed up big time
All coincidences aside, some of the bill’s rules have nothing to do with protecting borrowers, like the required $500,000 surety bond to become licensed for example. Compare that to California’s $25,000 licensed lender surety bond. And the restriction on being able to sell or securitize a loan, how does that help small businesses?
These requirements and others suggest that it’s about preventing all alternatives from existing in the marketplace, rather than predatory alternatives. The losers would undoubtedly be small businesses and the Illinois job market. Senator Collins and Treasurer Summers, both of whom have a strong track record of empowering their constituents financially, may have underestimated or overlooked the likely negative consequences of this bill.
The nonbanks
Several nonbank trade groups are reportedly in the process of formulating a response.
The Commercial Finance Coalition for example, a nonprofit coalition of financial technology companies, told AltFinanceDaily that they are concerned about the impact this will have on the Illinois job market and will indeed have representatives on the ground in Illinois.
They also wanted to make known that they welcome support from marketplace lenders, nonbanks and merchant cash advance companies in these efforts and that interested parties should email Mary Donahue at mdonohue@commercialfinancecoalition.com
To contact Senator Jacqueline Collins who introduced the bill, call her at 217-782-1607.
Industry Trade Group Coming of Age: The SBFA is Becoming More Political
February 1, 2016By hiring an executive director, the Small Business Finance Association hopes to achieve at least two goals – taking a step toward becoming a full-service trade group and providing a public voice for the alternative finance industry.
Stephen Denis, formerly deputy staff director of the U.S. House Committee on Small Business, went to work in the new role in mid-December, setting up shop with his cell phone and laptop in a Washington, DC, area coffee emporium. He’s the SBFA’s first full-time employee.
Hiring Denis, who also has association experience, represents “the next evolution” of the trade group, according to David Goldin, SBFA president and Capify’s founder, president and CEO.
 The SBFA, which got its start in 2008 as the North American Merchant Advance Association, changed its name last year because members have added small-business loans to the their merchant cash advance offerings. Although the trade group’s not exactly new, it has plenty of room to grow and its leadership and members seem open to change.
The SBFA, which got its start in 2008 as the North American Merchant Advance Association, changed its name last year because members have added small-business loans to the their merchant cash advance offerings. Although the trade group’s not exactly new, it has plenty of room to grow and its leadership and members seem open to change.
“The goal is to start from scratch and take a look at everything the association is doing,” Denis told AltFinanceDaily, “and to really build this out to a robust group that represents the interests of small businesses.”
Denis appears optimistic about pursuing that goal. He’s a native of the Boston area and a Harvard University graduate whose first job out of school was as an aide to Republican Sen. John E. Sununu of New Hampshire. After three years in that position, he took a job for two years with a UK-based trade association, traveling frequently to London to inform the group of Congressional action in the United States.
From there, Denis went on to become director of government affairs and economic development for the Cincinnati Business Committee, a regional association that included Fortune 500 companies among its members. After two years in that role, Denis joined the staff of Rep. Steve Chabot, R-Ohio, moving back to Washington and serving as the congressman’s deputy chief of staff during a five-year stint that ended when he joined the SBFA.
While working for Chabot, Denis also became deputy staff director of the House Committee for Small Business, the No. 2 position there, and he has held that job for the last three years. The committee’s tasks include learning as much as they can about small business, including financing, and using the information to advise members of the House on policy initiatives.
The experience Denis has amassed in government should serve the association well because his duties include briefing federal legislators and regulators on how the alternative-finance business works. With Denis as spokesperson, the industry can speak to government with a single voice, Goldin asserted.
“We are going to be aggressive in our outreach to legislators and regulators as well as be active reaching out to local, state governments,” Denis said. The SBFA will “work with other trade groups and small business groups to promote our mission to ensure small businesses have alternative finance options available to them.”

Until now, too many players from the alternative finance industry have been vying for lawmakers’ attention, Goldin said. To make matters worse, some of those seeking to influence government in hearings on Capitol Hill are brokers instead of lenders and thus may not have a perfect understanding of risk and other aspects of the business, he maintained.
“We’re hearing that there are people trying to be the voice of small-business finance that either don’t have a lot of years of experience or they’re not telling the whole story,” Goldin said. “We want to make sure the industry’s represented properly.”
Denis can draw attention away from the “noise” created by unqualified voices and focus on information that Congress needs to make reasonable decisions about the alternative finance business, Goldin maintained.
Besides getting the word out in Washington, the SBFA hopes to convey its message to the general public on “the benefits of alternative financing,” Goldin said. At the same time the group can help make small business owners aware of the finance options, Denis added.
 Asked whether hiring Denis marks the beginning of an effort to lobby members of Congress for legislation the association deems favorable to the industry, Goldin said only that additional announcements will be forthcoming.
Asked whether hiring Denis marks the beginning of an effort to lobby members of Congress for legislation the association deems favorable to the industry, Goldin said only that additional announcements will be forthcoming.
Meanwhile, updated “best practices” guidelines might be in the offing to help industry players navigate the business ethically and efficiently, Goldin said. A set of six best practices the association released in 2011 included clear disclosure of fees, clear disclosure of recourse, sensitivity to a merchants’ cash flow, making sure advances aren’t presented as loans and paying off outstanding balances on previous advances.
Addressing other possible steps in the association’s growth, Goldin said the group doesn’t plan to publish an industry trade magazine or newsletter. However, a trade show or conference might make sense, he noted.
Denis said he and the board had not discussed the possibility of a test, credential or accreditation to certify the expertise of qualified members of the industry. However, associations often establish and monitor such standards, so it would be reasonable for the SBFA to do so, he added.
The association might establish a Washington office, Goldin said. “We’ll look to Steve for his thoughts and guidance on that,” he observed. Denis seems amenable to the idea. “Down the road, we would love to open an office and hire more people,” he said.
In Goldin’s view, all of those moves might help the rest of the world comprehend the industry. Understanding the industry requires taking into account the cost of dealing with risk and business operations, he said.
Placing a $20,000 merchant cash advance, for example, requires a customer-acquisition effort that costs about $3,000 and a write-off of losses and overhead of about $4,000, Goldin said. That’s a total of $27,000 even without the cost of capital, he maintained.
“Most people don’t understand the economics of our business,” Goldin continued. The majority of placements are for less than $25,000, he said, characterizing them as “almost a loss leader when you factor in the acquisition costs.”
While spreading that type of information on the industry’s inner workings, Denis will also conduct the day-to-day for the not-for-profit’s affairs. The association’s board of directors will continue to set policy and objectives.
Members elect the board members to two-year terms. Current board members are Goldin; Jeremy Brown of Rapid Advance, who’s also serving as the group’s vice president; John D’Amico, GRP Funding; Stephen Sheinbaum, Bizfi; and John Snead, Merchants Capital Access.
Member companies include Bizfi, BFS Capital, Capify, Credibly, Elevate Funding, Fora Financial, GRP Funding, Merchant Capital Source, Merchants Capital Access (MCA), Nextwave Funding, NLYH Group LLC, North American Bancard, Principis Capital, Rapid Advance, Strategic Funding Source and Swift Capital.
Companies pay $3,000 in monthly dues, which Denis characterizes as inexpensive for a DC-based trade association.
Membership could spread to other types of businesses, Denis said. “I’d like to expand the tent to other industries,” he noted. “The association is trying to represent the interests of small business and make sure they have every finance option available to them.”
But a key purpose of the trade association is to provide a forum for members to come together as an industry, Denis said. “We’re thinking big,” he admitted. “We hope that all members of the marketplace will want to become a part of it.”
Year of The Broker Concludes – 2015 Recap
December 31, 2015 It was the Year of the Broker, a phrase that often conjured up images of easy money and inexperience. Lenders like OnDeck reacted by reducing their dependence on them. Responsible for 68.5% of their deal flow in 2012, OnDeck only sourced 18.6% of their deals from brokers in the third quarter of 2015.
It was the Year of the Broker, a phrase that often conjured up images of easy money and inexperience. Lenders like OnDeck reacted by reducing their dependence on them. Responsible for 68.5% of their deal flow in 2012, OnDeck only sourced 18.6% of their deals from brokers in the third quarter of 2015.
But there’s money being made. One broker is on pace to do more than $100 million worth of deals annually after working as a plumber eight years ago. Another went from sleeping in his car to driving a Ferrari. Meanwhile, brokers like John Tucker are basically saying just the opposite. Tucker has repeatedly taken to AltFinanceDaily to preach things like “minimalism,” a practice of living below your means to a point where you can survive, and telling everyone it’s okay to embrace the satisfaction of a middle class life.
So is it the end of days or just the beginning?
In October, initial survey results of top industry CEOs revealed a confidence index of 83.7 out of 100, but out there on the street for the little guy, it’s been a tumultuous year. Things like commission chargebacks have hit brokers at unexpected times, with several funders privately telling us over the year that rogue brokers have closed their bank accounts or frozen the ACH debits in order to avoid giving the commissions back.
In 2015, brokers sued their sales agents and sales agents sued their employing brokers. Deals got backdoored, deals got co-brokered, and soliciting deals anonymously got banned from industry forums. Stacking continued mostly unfettered but is being pursued in the court system by funders allegedly injured by it. Brokers took over Wall Street and are supposedly being watched by regulators. Oh, and robo-dialing? Brokers should probably steer clear of that, just as underwriters should ditch paper bank statements.
It’s a lot to manage. Sometimes for a broker, just losing a deal can make them so sick that they have to go home. That’s apparently what happens when you don’t answer the phone fast enough. At least one said there’s no room left for more competitors so if you were thinking of starting a brokerage now, $2,000 won’t be enough.
But things could be worse. In 2015, IOU Financial was under attack by Russian nuclear scientists, a story that was more truth than exaggeration. In the end, Qwave Capital acquired a 15% stake in IOU.
An OnDeck class action lawsuit that looked bad at first turned out to be mostly based on the words of a convicted stock manipulator with a short position in the stock. The case is still ongoing and OnDeck’s stock price is down 50% from their IPO.
In 2015, two guys lost God but found $40 million (although numerous sources say that number is off).
“Madden” no longer means the football video game and Section 1071 is not a seating area in a stadium.
An RFI turned out to be something not to LOL about. Despite an overwhelming response from lenders and funders, the Treasury isn’t completely sold.
 Things weren’t so automated in 2015 despite the cries of technological disruption. Maybe that’s why it feels like 1997. Manual underwriting still dominated and bank statements still matter as much as they ever did. God declined loan applications, Google rigged the search results, and a mayor declared war on merchant cash advance (and then never spoke about it ever again after being re-elected).
Things weren’t so automated in 2015 despite the cries of technological disruption. Maybe that’s why it feels like 1997. Manual underwriting still dominated and bank statements still matter as much as they ever did. God declined loan applications, Google rigged the search results, and a mayor declared war on merchant cash advance (and then never spoke about it ever again after being re-elected).
Lobbying coalitions formed. NAMAA became the SBFA. The CFPB lied and community bankers testified.
But things are looking up. Brokers can obtain outside investments, get acquired, or make millions through syndication.
Bad Merchants are now ending up in more than one bad database, though a deal for the ages slipped through the cracks. Other merchants went to jail. Square went public and brought merchant cash advances along with them. The industry beamed its message through Times Square and one Democratic congressman has asked God to bless it all.
It was a crazy year. Marketplace lending became an acknowledged term (and the name of a conference) and already companies under that umbrella have been linked to presidential candidate (and desperate loser) Jeb Bush and the San Bernardino Terrorists. The FDIC had a few things to say and SoFi went triple-A. Marketplace lending is making a lot of people money, but when looking at the tax implications is there something funny?
In 2015, the big boys shared their wisdom and their figures. Turns out, it was beyond hyperbole. Brokers experienced an incredible rise or they pawned their ferrari to the other guys. Some focused on a specific crop, while others are trying it over the top. California sucked, John Tucker tucked, and one lender got totally F*****. In 2015 some funders got tanked, so in 2016 we’ll all be AltFinanceDaily.
Happy New Year!
Bizfi Secures $65 Million in Financing
December 15, 2015NEW YORK–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Bizfi (www.bizfi.com), the premier FinTech company whose online small business finance platform combines aggregation, funding and a participation marketplace, announced that Metropolitan Equity Partners (“Metropolitan”) has provided a structured financing facility of $65 million to the company to drive growth.
Closing this financing round enables Bizfi to:
- Expand its suite of funding programs, increasing its ability to fund America’s small business capital needs.
Increase the speed at which funding applicants access direct financing from Bizfi. - Develop and implement a national marketing campaign designed to increase the awareness of the Bizfi brand and platform within the small to medium-sized business community.
- Bizfi and its proprietary marketplace and funding technologies have provided in excess of $1.3 billion in financing to over 26,000 small businesses across the United States since 2005. Since Bizfi launched its aggregation platform in 2015, the Company has experienced 72% growth in year-over-year gross originations.
“The Bizfi platform is the simplest, fastest and most frictionless process for small businesses to access funding. Metropolitan’s financing will propel our growth plans to the next stage,” said Stephen Sheinbaum, founder of Bizfi. “Every day more and more businesses are turning to Bizfi because of our strong channel partners, enabling business owners to compare all their funding options in one place. The Metropolitan partnership provides Bizfi with additional capital to develop new products and fund more small businesses from its own branded product set.”
Metropolitan’s investment provides the financial flexibility and strength to support Bizfi’s growth plans. The new investment expands upon Metropolitan’s prior involvement as an active buyer of loan participations and a mezzanine lender to the Company for the past three years.
Bizfi’s proprietary technology and aggregation platform efficiently gathers applicant information from a wide variety of sources to quickly offer commercial funding products including loans and other capital products to small businesses. Bizfi’s technology is further strengthened by strategic relationships with more than 45 funding partners, including OnDeck, Funding Circle, IMCA Capital, Bluevine and Kabbage. Bizfi also participates as a lender on the platform. Regardless of what kind of capital is sought from any of the funding partners, the small business owner is guided through the entire process by a Bizfi funding concierge that is assigned specifically to him or her.
Paul Lisiak, managing partner of Metropolitan Equity Partners stated, “Metropolitan believes that the future of small business lending is being built by Bizfi. Their aggregation and direct lending marketplace is disrupting the fast growing FinTech industry. Our new investment is the result of the impressive performance we have directly experienced as a lender and participant in the company’s financing products over the past three years. In the rapidly evolving FinTech space, Bizfi’s management team has elegantly expanded their product offerings to create a platform that holistically meets the dynamic funding needs of small businesses. We look forward to being a part of Bizfi as they further solidify their position as a leader in the financial technology space.”
Metropolitan has been an active investor in the alternative lending and FinTech space with over $100 million committed in 2015 including investments in JH Capital Group, Debt Away, New Credit America and PledgeCap.
Mr. Sheinbaum concluded, “Bizfi has seen radical growth over the last 18 months. Not only have we developed one of the most robust FinTech platforms for the small business lending space, but we have cultivated significant deals with third party companies that service small businesses. These companies will utilize white label versions of Bizfi’s platform to offer financing to their clients. Now, with the Metropolitan financing supporting our growth, we can continue to expand our products, increase our market share and provide solutions to the critical financing needs of the companies that fuel our economy.”
About Bizfi
Bizfi, is the premier FinTech company combining aggregation, funding and a participation marketplace on a single platform for small businesses. Founded in 2005, Bizfi and its family of companies have provided more than $1.3 billion in financing to over 26,000 small businesses in a wide variety of industries across the United States.
Bizfi’s connected marketplace instantly provides multiple funding options to businesses from more than 45 funding partners and real-time pre-approvals. Bizfi’s funding options include short-term financing, medical financing, lines of credit, equipment financing, invoice financing, medium-term loans and long-term loans guaranteed by the U.S. Small Business Administration. The Bizfi API provides a turnkey white label or co-branded solution that easily allows strategic partners to access the Bizfi engine and present their clients with financial offers from Bizfi lenders all while maintaining their customer’s user experience. A process that once took hours, now takes minutes.
About Metropolitan Equity Partners
Metropolitan Equity Partners Management, LLC is an alternative investment manager that provides expansion capital to growing private companies via collateralized loan structures. Metropolitan was founded by Paul Lisiak who has 20 years of experience investing in private U.S companies through both debt and equity. Metropolitan traces its roots to a successful equity strategy managed by the current Metropolitan Principals which was backed by the Man Group plc. Since 2008, Metropolitan has committed over $300MM in collateralized debt investments through call funds, blind pools and institutional managed accounts. Metropolitan is based in New York City.
Contacts
KCSA Strategic Communications
Abbie Sheridan, 212-896-1207
asheridan@kcsa.com
or
Kenneth Cousins, 212-896-1254
kcousins@kcsa.com
or
Bizfi Sales:
855-462-4934
bizfisales@bizfi.com
or
Bizfi Marketing:
212-545-3182
marketing@bizfi.com
Alternative Business Funding’s Decade Club
October 22, 2015 The working capital business is a very different animal now than it was a decade or so ago when many of today’s established players were just starting out.
The working capital business is a very different animal now than it was a decade or so ago when many of today’s established players were just starting out.
“At that time, the industry was a bunch of cowboys. It was an opportunistic industry of very small players,” says Andy Reiser, chairman and chief executive of Strategic Funding Source Inc., a New York-based alternative funder that’s been in business since 2006. “The industry has gone from this cottage industry to a professionally managed industry.”
Indeed, the alternative funding industry for small businesses has grown by leaps and bounds over the past decade. To put it in perspective, more than $11 billion out of a total $150 billion in profits is at risk to leave the banking system over the next five plus years to marketplace lenders, according to a March research report by Goldman Sachs. The proliferation of non-bank funders has taken such a huge toll on traditional lenders that in his annual letter to shareholders, J.P. Morgan Chase & Co. chief executive officer Jamie Dimon warned that “Silicon Valley is coming” and that online lenders in particular “are very good at reducing the ‘pain points’ in that they can make loans in minutes, which might take banks weeks.”
The burgeoning growth of alternative providers is certainly driving banks to rethink how they do business. But increased competition is also having a profound effect on more seasoned alternative funders as well. One of the latest threats to their livelihood is from fintech companies, like Lendio and Fundera,for example, that are using technology to drive efficiency and gaining market share with small businesses in the process.
“Established lenders who want to effectively compete against the new entrants will need to automate as much decisioning as possible, diversify acquisition sources and ensure sufficient growth capital as a means to capture as much market share as possible over the next 12 to 18 months,” says Kim Anderson, chief executive of Longitude Partners, a Tampa-based strategy consulting firm for specialty finance firms.
Of course, there is truth to the adage that age breeds wisdom. Established players understand the market, have a proven track record and have years of data to back up their underwriting decisions. At the same time, however, experience isn’t the only factor that can ensure a company will continue to thrive over the long haul.
WORKING TOWARD THE FUTURE
Indeed, established players have a strong understanding of what they are up against—that they can’t afford to live in the glory of the past if they want to survive far into the future.
“With every business you have to reinvent yourself all the time. That’s what a successful business is about,” says Reiser of Strategic Funding. “You see so many businesses over the years that didn’t reinvent themselves, and that’s why they’re not around.”
Strategic Funding has gone through a number of changes since Reiser, a former investment banker, founded it with six employees. The company, which has grown to around 165 employees, now has regional offices in Virginia, Washington and Florida and has funded roughly $1 billion in loans and cash advances for small to mid-sized businesses since its inception.
One of the ways Strategic Funding has tried to distinguish itself is through its Colonial Funding Network, which was launched in early 2009. CFN is Strategic Funding’s secure servicing platform which enables other companies who provide merchant cash advances, business loans and factoring to “white label” Strategic Funding’s technology and reporting systems to operate their businesses.
“When you’re in a commodity-driven business, you have to find something to differentiate yourself,” Reiser says.
FINDING WAYS TO BE DIFFERENT
That’s exactly what Stephen Sheinbaum, founder of Bizfi (formerly Merchant Cash and Capital) in New York, has tried to do over the years. When the company was founded in 2005, it was solely a funding business. But over the years, it has grown to around 170 employees and has become multi-faceted, adding a greater amount of technology and a direct sales force. Since inception, the Bizfi family of companies has originated more than $1.2 billion in funding to about 24,000 business owners.
 Earlier this year, the company launched Bizfi, a connected online marketplace designed specifically to help small businesses compare funding options from different sources of capital and get funded within days. Current lenders on the platform include Fundation, OnDeck, Funding Circle, CAN Capital, SBA lender SmartBiz, as well as financing from Bizfi itself. Financing options on the platform include short-term funding, equipment financing, A/R financing, SBA loans and medium term loans.
Earlier this year, the company launched Bizfi, a connected online marketplace designed specifically to help small businesses compare funding options from different sources of capital and get funded within days. Current lenders on the platform include Fundation, OnDeck, Funding Circle, CAN Capital, SBA lender SmartBiz, as well as financing from Bizfi itself. Financing options on the platform include short-term funding, equipment financing, A/R financing, SBA loans and medium term loans.
Sheinbaum credits newer entrants for continually coming up with new technology that’s better and faster and keeping more established funders on their toes.
“If you don’t adapt, you die,” he says. “Change is the one constant that you face as a business owner.”
David Goldin, chief executive of Capify, a New York-based funder, has a similar outlook, noting that the moment his company comes out with a new idea, it has to come up with another one. “If you’re not constantly innovating you’re in trouble,” he says. “It’s a 24/7 global job.”
Capify, which was known as AmeriMerchant until July, was founded by Goldin in 2002 as a credit card processing ISO. In 2003, the company began focusing all of its efforts on merchant cash advances. Four years later, the company made its first international foray by opening an office in Toronto. The company continued to expand its international presence by opening up offices in the United Kingdom and Australia in 2008. The company now has more than 200 employees globally and hopes to be around 300 or more in the next 12 months, Goldin says. The company has funded about $500 million in business loans and MCAs to date, adjusted for currency rates.
THE CULTURE OF CHANGE
Five or six years ago, Capify’s main competitors were other MCA companies. Now the competition primarily comes from fintech players, and to keep pace Capify has made certain changes in the way it operates. From a human resources standpoint, for instance, Capify switched from business casual attire to casual dress in the office. The company has also been doing more employee-bonding events to make sure morale remains high as new people join the ranks. “We’ve been in hyper-growth mode,” he says.
CAN Capital in New York, another player in the alternative small business finance space with many years of experience under its belt, has also grown significantly (and changed its name several times) since its inception in 1998. The company which began with a handful of employees now has about 450 and has offices in NYC, Georgia, Salt Lake City and Costa Rica. For the first 13 years, the company focused mostly on MCA. Now its business loan product accounts for a larger chunk of its origination dollars.
This year, the company reached the significant milestone of providing small businesses with access to more than $5 billion of working capital, more than any other company in the space. To date, CAN Capital has facilitated the funding of more than 160,000 small businesses in more than 540 unique industries.
Throughout its metamorphosis to what it is today, the company has put into place more formalized processes and procedures. At the same time, the company has tried very hard to maintain its entrepreneurial spirit, says Daniel DeMeo, chief executive of CAN Capital.
One of the challenges established companies face as they grow is to not become so rule-driven that they lose their ability to be flexible. After all, you still need to take calculated risk in order to realize your full potential, he explains. “It’s about accepting failure and stretching and testing enough that there are more wins than there are losses,” says DeMeo who joined the company in March 2010.
ADVICE FOR NEWCOMERS
As the industry continues to grow and new alternative funders enter the marketplace, experience provides a comfort level for many established players.
“The benefit we have that newcomers don’t have is 10 years of data and an understanding of what works and what doesn’t work,” says Reiser of Strategic Funding. With the benefit of experience, Reiser says his company is in a better position to make smarter underwriting decisions. “There are many industries we funded years back that we wouldn’t touch today for a variety of reasons,” he says.
Experienced players like to see themselves as role models for new entrants and say newcomers can learn a lot from their collective experiences, both good and bad. Noting the power of hindsight, Reiser of Strategic Funding strongly advises newcomers to look at what made others in the business successful and internalize these best practices.
One of the dangers he sees is with new companies who think their technology is the key to long-term survival. “Technology alone won’t do it because that too will become a commodity in time,” he says.
Over the years Strategic Funding has learned that as important as technology is, the human touch is also a crucial element in the underwriting process. For example, the last but critical step of the underwriting process at Strategic Funding is a recorded funding call. All of the data may point to the idea that a particular would-be borrower should be financed. But on the call, Strategic Funding’s underwriting team may get a bad vibe and therefore decide not to go forward.
“We look at the data as a tool to help us make decisions. But it’s not the absolute answer,” Reiser says. “We are a combination of human insight and technology. I think in business you need human insight.”
Seasoned alternative funding companies also say that newbies need to implement strong underwritingcontrols that will enable them to weather both up and down markets.
The vast majority of newcomers have never experienced a downturn like the 2008 Financial Crisis, which is where seasoned alternative financing companies say they have a leg up. Until you’ve lived through down cycles, you’re not as focused as protecting against the next one, notes Sheinbaum of Bizfi. “Every 10 years or 15 years or so, there seems to be a systemic crisis. It passes. You just have to be ready for it,” he says.
Goldin of Capify believes that many of today’s start-ups don’t understand underwriting and are throwing money at every business that comes their way instead of taking a more cautious approach. As a funder that has lived through a down market cycle, he’s more circumspect about long-term risk.
 One of the biggest problems he sees is funders who write paper that goes two or three years out. His company is only willing to go out a maximum of 15 months for its loan product, which he believes is s a more prudent approach. He questions what will happen when the economy turns south—as it eventually will—and funders are stuck with long dated receivables. “You’re done. You’re dead. You can’t save those boats. They are too far out to sea,” Goldin says.
One of the biggest problems he sees is funders who write paper that goes two or three years out. His company is only willing to go out a maximum of 15 months for its loan product, which he believes is s a more prudent approach. He questions what will happen when the economy turns south—as it eventually will—and funders are stuck with long dated receivables. “You’re done. You’re dead. You can’t save those boats. They are too far out to sea,” Goldin says.
Having a solid capital base is also a key to long-term success, according to veteran funders. Many of the upstarts don’t have an established track record and need to raise equity capital just to stay afloat—an obstacle many long-time funders have already overcome.
Goldin of Capify believes that over time consolidation will swallow up many of the newbies who don’t have a good handle on their business. Hethinks these companies will eventually be shuttered by margin compression and defaults. “It can’t last like this forever,” he says.
In the meantime, competition for small business customers continues to be fierce, which in turn helps keep seasoned players focused on being at the top of their game. Getting too comfortable or complacent isn’t the answer, notes DeMeo of CAN Capital. Instead, established funders should seek to better understand the competition and hopefully surpass it. “Competition should make you stronger if you react to it properly,” he says.
Fake Business Loan Application Fees Leads to Two Convictions
October 5, 2015 Two men were convicted last week of perpetrating an advance fee fraud scheme. David C. Jackson and Alexander D. Hurt defrauded more than 40 individuals out of $4.5 million, mainly by directing small businesses hoping to get a loan to pay phony application fees, collateral fees, or commitment fees. “These defendants and their co-conspirators took advantage of individuals and business owners who had limited options in acquiring business loans in the difficult financial environment that existed after the recession of 2008,” states a report issued by the Department of Justice.
Two men were convicted last week of perpetrating an advance fee fraud scheme. David C. Jackson and Alexander D. Hurt defrauded more than 40 individuals out of $4.5 million, mainly by directing small businesses hoping to get a loan to pay phony application fees, collateral fees, or commitment fees. “These defendants and their co-conspirators took advantage of individuals and business owners who had limited options in acquiring business loans in the difficult financial environment that existed after the recession of 2008,” states a report issued by the Department of Justice.
Deirdre M. Daly, United States Attorney for the District of Connecticut, said that people need to be careful about loan offers online. “Those seeking business loans need to be wary of any provider of funding that requires significant fees in advance—especially those who use the Internet to prey upon trusting people who are unable to verify the representations made,” Daly said.
“Jackson was previously convicted of federal bank fraud and money laundering offenses in October 2006 and was sentenced to 41 months in prison, followed by five years of supervised release,” the DOJ report says. “He was released from federal prison in September 2009 and operated this advance fee fraud scheme while on supervised release.”
The two used a slew of personal aliases and business names to cover their trail. The business names included:
- Jalin Realty Capital Advisors, LLC
- American Capital Holdings, LLC
- Brightway Financial Group, LLC
An archived version of American Capital Holding’s website said the following on the home page:
“In today’s economic climate, finding reliable funding sources can be frustrating. Fortunately, we are partnered with an investment fund that provides commercial real estate development and acquisition projects. Due to our professionalism & honesty we have achieved massive trust worldwide.”
One lesson here would be to cautious of anyone who says they have “achieved massive trust” but another is to conduct background checks on the online lender you’re considering.
And of course never pay a fee upfront for the promise of a loan in return.
Alternative Funding: Over The Top Down Under
September 2, 2015 San Francisco had its gold rush, Oklahoma had its land rush and now Australia is experiencing a rush of alternative funding. After a slow start a few years ago, foreign and domestic companies have been flocking to the market down under in the last 18 months.
San Francisco had its gold rush, Oklahoma had its land rush and now Australia is experiencing a rush of alternative funding. After a slow start a few years ago, foreign and domestic companies have been flocking to the market down under in the last 18 months.
As many as 20 new alt-funders are doing business in Australia, but that number could swell to a hundred, said Beau Bertoli, joint CEO of Prospa, a Sydney-based alternative funder. “The market in Australia has been very ripe for alternative finance,” Bertoli, said. “We see an opportunity for the alternative finance segment to be more dominant in Australia than it is in America.”
Recent entrants to the embryotic Australian market include Spotcap, a Berlin-based company partly funded by Germany’s Rocket Internet; Australia’s Kikka Capital, which gets tech backing from U.S.-based Kabbage; America’s Ondeck, which is working with MYOB, a software company; Moula, which began offering funding this year but considers itself ahead of the curve because it formed two years ago; and PayPal, the giant American payments company.
The new entrants are joining ‘pioneers’ that have been around a few years, like Prospa, which has been working for three years with New York-based Strategic Funding Source, and Capify (formerly AUSvance until it was consolidated into the international brand Capify), which came to market in 2008 with merchant cash advances and started offering small-business loans in 2012.
Some don’t take the newcomers that seriously. “There are small players I’ve never heard of,” said John de Bree, managing director of Capify’s Sydney-based office, in a reference to local Australian funders. “The big ones like OnDeck and Kabbage don’t have the local experience.”
But many players view the influx as a good sign. “I think it’s an endorsement of the market,” Bertoli said. “There’s more publicity and more credibility for what we’re doing here in terms of alternative finance.” It’s like the merchant who gets more business when a competing store opens across the street.
Besides, the market remains far from crowded. “I’m not concerned about the arrival of OnDeck and Kabbage because it really does validate our model,” maintained Aris Allegos, who serves as Moula CEO and cofounded the company with Andrew Watt.
The market’s relatively small size – at least compared to the U.S. – doesn’t seem to bother players accustomed to the heavily populated U.S., a development some observers didn’t expect. “I’m very surprised,” de Bree said of the American interest in Australia. “The American market’s 15 times the size of ours.”
Others see nothing but potential in Australia. “This is a market that will evolve over time, and we think the opportunity is enormous,” said Lachlan Heussler, managing director of Spotcap Australia.
Some view the Australian rush to alternative finance not so much as a solitary phenomenon but instead as part of a worldwide explosion of interest in the segment, driven by banks’ reluctance to provide loans since the financial crisis, de Bree said.
Viewed independently or in a larger context, the flurry of activity in Australia is new. “The boom is probably only getting started,” Bertoli maintained in a reference to the Australian market. “Right now, it’s about getting the foundation of the market established.”
To get the business underway in Australia, alternative funders are alerting small-business owners and the media to the fact that alternative funding is becoming available and teaching them how it works, de Bree said. “Half of our job is educating the market,” noted Heussler.
New players are building the track record they need to bring down the cost of funds, according to Allegos. “Our base rate is 2 percent or 3 percent higher than yours,” he said, adding that the cost of funds is more challenging than gearing up the tech side of the business.
Although the alternative-lending business started later in Australia than in the United States and lags behind America in in exposure, it’s maturing rapidly, said de Bree. Aussie funders are benefitting from the lessons their counterparts have learned in the U.S., he said.
 But the exchange of information flows both ways. Kabbage, for example, chose to enter the Australian market with a local partner, Kikka. Kabbage learned from its earlier foray into the United Kingdom that it makes sense to work with colleagues who understand the local regulatory system and culture, said Pete Steger, head of business development for Atlanta-based Kabbage.
But the exchange of information flows both ways. Kabbage, for example, chose to enter the Australian market with a local partner, Kikka. Kabbage learned from its earlier foray into the United Kingdom that it makes sense to work with colleagues who understand the local regulatory system and culture, said Pete Steger, head of business development for Atlanta-based Kabbage.
Such differences mean that risk-assessment platforms that work in the United States or Europe require localization before they can perform effectively in Australia, sources said.
Sydney-based Prospa, for example, got its start three years ago and has been working ever since with New York-based Strategic Funding Source to localize the SFS American risk-assessment platform for Australia, said Bertoli, who shares the company CEO title with Greg Moshal.
Moula, which has headquarters in Melbourne, sees so many differences among markets that it decided to build its own local platform from scratch, according to Allegos.
One key difference between the two markets is that Australia does not have positive credit reporting. “We have nothing that even comes close to a FICO score,” said Allegos. The only credit reporting centers on negative events, he said.
Without credit scores from credit bureaus, funders base their assessments of credit worthiness largely on transaction history. “It’s cash-flow analytics,” said Allegos. “It’s no different from the analysis you’re doing in your part of the world, but it becomes more significant” in the absence of positive credit reporting, he said.
Australia lacks credit scores at least partly because the country’s four main banks control most of the financial sector and choose not to release credit information, sources said. The banks have warded off attacks from all over the world because the regulatory environment supports them and because their management understands how to communicate with and sell to Australian customers, sources said.
The big banks – Commonwealth Bank, Westpac, Australia and New Zealand Banking Group, and National Australia Bank – set their own rules and have kept money tight by requiring secured loans and long waiting periods, Bertoli said. It’s difficult for merchants who don’t fit into a “particular box” to procure funding, he maintained. “It’s almost like an oligarchy,” Allegos said of the banks’ grip on the financial system.
Eventually, the banks may form partnerships with alternative lenders, but that day won’t come soon, in Allegos’ estimation. It could be 12 months or more away, he said.
Even as the financial system evolves, deep-seated differences will remain between Australia and the U.S. Most Americans and Australians speak English and share many views and values, but the cultures of the two countries differ greatly in ways that affect marketing, Bertoli said. “In your face” advertising that can work well with “loud, confident” Americans can offend the more “laid-back” Australian consumers and business owners, he said.
Australians have become tech-savvy and comfortable with online banking, but they guard their privacy and often hesitate to reveal their banking information to a funding company, Allegos said. The entrance of OnDeck and Kabbage should help familiarize potential customers with the practice of sharing data, he predicted.
Cost structures for businesses differ in Australia from the U.S., Bertoli noted. Australian companies pay higher rent and have to pay minimum wages set much higher than in the United States, he said. Published reports set the Australian minimum wage at $13.66 U.S. dollars. The higher costs down under can take a toll on cash flow. “Take an American scorecard and apply it to Australia?” Bertoli asked rhetorically. “You just can’t.”
 Distribution’s not the same for commercial enterprises in the two countries, Bertoli maintained. Despite having about the same geographic area as America’s 48 contiguous states, Australia has a population of 23 million, compared with America’s 322 million.
Distribution’s not the same for commercial enterprises in the two countries, Bertoli maintained. Despite having about the same geographic area as America’s 48 contiguous states, Australia has a population of 23 million, compared with America’s 322 million.
No matter how many people are involved, changing their habits takes time. Australian merchants prefer fixed-term loans or lines of credits instead of merchant cash advances, Bertoli said. In many cases Australian merchants simply aren’t as familiar as Americans are with advances, Allegos said.
Besides, the four big banks in Australia tend to solicit merchants for credit and debit card transactions without the help of the independent sales organizations and sales agents. In the U.S., ISOs and agents play an important role in explaining and promoting advances to merchants, Bertoli said. Advances make sense for merchants because advances adjust to cash flow, and they help funders control risk, but just haven’t caught on in Australia, Bertoli said. Australians resist advances if too many fees are attached, said Allegos.
Pledging a portion of daily card receipts might seem too frequent, too, he said. Besides, advances are limited to merchants who accept debit and credit cards, while any business could conceivably choose to take out a loan, said de Bree.
Advances have to compete with inventory factoring, which has become a massive business in Australia, according to Heussler. The business can become intrusive because funders may have to examine balance sheets and talk to customers, he said.
Australia’s reluctance to turn to advances, leaves most alternative funders promoting loans and lines of credit. Prospa, for example, uses some brokers to that end but also relies on online connections, direct contact with customers, and referrals from companies that buy and sell with small and medium-sized businesses.
“Anyone that touches a small business is a potential partner,” said Heussler, including finance brokers, accountants, lawyers and even credit unions, which have the distribution but not the product.
Moula finds that most of its business comes from well-established companies and that loans average just over $27,000 in U.S. currency and they offer loans of up to more than $77,000 U.S. The company offers straight-line, six- to 12-month amortizing loans.
Using a model that differs from what’s common in the U.S., Moula charges 1 percent every two weeks, collects payments every two weeks and charges no additional fees, Allegos said. A $10,000 (Australian) loan for six months would accrue $714 (Australian) in interest, he noted.
 Spotcap Australia offers a three-month unsecured line of credit and doesn’t charge customers for setting it up, Heussler said. If the business owner decided to draw down, it turns into a six-month amortizing business loan for up to $100,000 Australian. Rates vary according to risk, starting at half a percent per month but averaging 1.5% per month.
Spotcap Australia offers a three-month unsecured line of credit and doesn’t charge customers for setting it up, Heussler said. If the business owner decided to draw down, it turns into a six-month amortizing business loan for up to $100,000 Australian. Rates vary according to risk, starting at half a percent per month but averaging 1.5% per month.
If companies have all of the necessary information at hand, they can complete an application in 10 minutes, Allegos said. Moula has to research some applications offline if the company’s structure deviates too greatly from the usual examples – much the same as in the U.S., he maintained. The latter requires strong customer-service departments, he said.
Kikka uses a platform based on the Kabbage model, which gives 95 percent of customers a 100-percent automated experience, Steger said. “It goes to show the power of our automation, our algorithms and our platform,” he maintained.
Spotcap prefers to deal with businesses that have been operating for at least six months, Heusler said. The funder examines records for Australia’s value-added tax and other financials, and it likes to connect with the merchant’s bank account. Spotcap can usually gain access to the account information through cloud-based accounting systems and thus doesn’t require most companies to download a lot of financial documents, he noted.
Despite the differences between the two countries, banking regulations bear similarities in Australia and the United States, sources said. In both nations the government tries harder to protect consumers than businesses because they assume business owners are more financially savvy. For consumers, regulators scrutinize length of term and pricing, sources said, and on the commercial side the government is concerned about money laundering and privacy.
Regulation of commercial funding will probably intensify, however, to ward off predatory lending, Bertoli said. Government will consult with businesses before imposing rules, he said. A couple of alternative business funders aren’t transparent with their pricing and they charge several fees – that sort of behavior will encourage regulation, Allegos said.
“I know they’re watching us – and watching us very closely,” he added.
In general, however, the Australian government supports alternative finance, Bertoli said, because they want there to be options other than the four big banks and wants small business to have access to capital. Small businesses account for 46 percent of economic activity in Australia and employ 70 percent of the workforce, he noted, saying that “if small businesses are doing badly, the economy is doing badly.”
Hence the need, many in the industry would say, for more alternative funding options in Australia.
Investing in the Industry: Break Out of Your Bubble
June 29, 2015 Even if you’re already working in alternative lending and know a lot about your particular area, the industry is growing by leaps and bounds and you might be feeling a little overwhelmed by the multitude of investment opportunities. Amid all the options, finding the right place to invest your money can feel as challenging as picking out the proverbial needle in a haystack.
Even if you’re already working in alternative lending and know a lot about your particular area, the industry is growing by leaps and bounds and you might be feeling a little overwhelmed by the multitude of investment opportunities. Amid all the options, finding the right place to invest your money can feel as challenging as picking out the proverbial needle in a haystack.
“Most people don’t know everything that’s out there. There are huge opportunities,” says Peter Renton, an investor and analyst who founded Lend Academy LLC of Denver, Colorado, a popular resource for the online lending industry.
Indeed, there are a growing number of online alternative lending sites that theoretically allow a person to invest in all shapes and sizes of loans. There are sites like Lending Club and Prosper that allow smaller investors to tap into the burgeoning P2P market. There are also a plethora of platforms that cater only to wealthier, more sophisticated investors in a host of areas like small business, real estate, student loans and consumer loans.
Even though there is a surplus of options, prudent investing is not quite as simple as depositing ample funds in an account and clicking the “go” button. Before you get started, you need to carefully consider factors such as your own finances and risk tolerance. You should also have a good handle on the specifics about the online platform—how it works, its history and track record, the types of investments it offers, the platform’s management team, technology and your ability to diversify based on available investment opportunities.
One of the first things you’ll have to think about as a potential investor is whether you have the financial wherewithal to be considered accredited by the SEC. If the answer’s yes, you’ll have a lot more choices of online marketplaces to choose from as well as types of investments. Basically, to meet the SEC’s threshold, you’ll need to have earned income that exceeded $200,000 (or $300,000 together with a spouse) in each of the prior two years, and reasonably expect to earn the same for the current year. Alternatively, you need to have a net worth over $1 million, either alone or together with a spouse (excluding the value of your home). (Check out the SEC’s website for more detailed info.)
 If you don’t fit the definition of accredited investor, it’ll be more difficult for you to find out about all the investment possibilities that are on the market today. That’s because the platforms that cater to accredited investors aren’t allowed by SEC rules to solicit, so many online marketplaces are hesitant to say much of anything for fear their words will be misconstrued by regulators as an attempt to drum up new business. With limited exceptions, you won’t be able to get more than very basic information from and about these platforms’ unless you are accredited.
If you don’t fit the definition of accredited investor, it’ll be more difficult for you to find out about all the investment possibilities that are on the market today. That’s because the platforms that cater to accredited investors aren’t allowed by SEC rules to solicit, so many online marketplaces are hesitant to say much of anything for fear their words will be misconstrued by regulators as an attempt to drum up new business. With limited exceptions, you won’t be able to get more than very basic information from and about these platforms’ unless you are accredited.
But smaller investors do have options. Two San Francisco-based online lending platforms, Lending Club and Prosper, cater to individual investors, and you can still make a pretty penny plunking down money with these venues. You’ll also find a wealth of information about investing with them by perusing their websites as well as by reading the blog posts of media-savvy financiers.
“Right now, Lending Club and Prosper provide a great entry point for people who want to get involved in investing in alternative lending,” says Renton of Lend Academy.
The caveat is that these platforms aren’t yet open to investors in every state, so if yours isn’t on the list you’re out of luck for now. However, with each marketplace you’ve got more than a 50 percent chance your state is on the approved list, so it’s worth digging deeper.
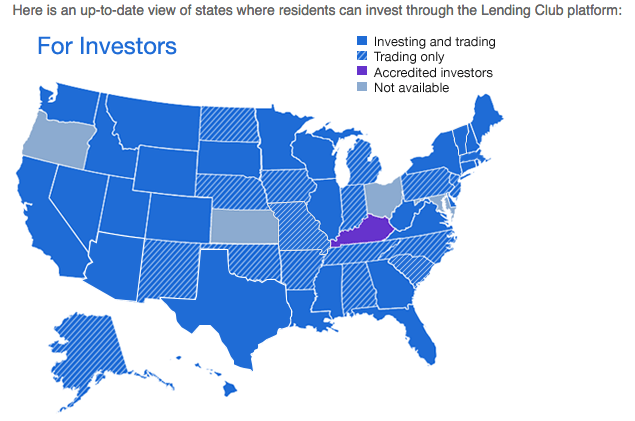
Assuming you meet their respective suitability requirements, you can choose to invest on one platform or both. To be sure, they are alike in many ways. Both allow you to invest with as little as $25 and fund one loan, however they recommend you buy at least 100 loans to be properly diversified, which you can do for as little as $2,500. You can manually choose which loans to buy, or enter your investment criteria so loan picking is automated. You can also invest retirement money in an IRA through Lending Club or Prosper.
There’s no fee to get started investing on either platform. For Lending Club, investors pay a service fee equal to 1 percent of the amount of payments received within 15 days of the payment due date. Prosper charges investors 1% per year on the outstanding balance of the loan. As the loan gets smaller, the servicing fee, which is charged monthly, gets smaller too.
To invest in Lending Club, in most cases you’ll need either $70,000 in income and a net worth of at least $70,000, or a net worth of at least $250,000. There may be other financial suitability requirements that vary slightly depending on the state you live in. For Prosper, individual investors must be United States residents who are 18 years of age or older and have a valid Social Security number.
At any given time, Lending Club has more than 1,000 loans visible on the platform and new ones get added every day, according to Scott Sanborn, chief operating officer and chief marketing officer. Prosper, meanwhile, on average has more than 200 loans for people to invest in, says Ron Suber, president.
 Returns tend to be favorable compared with other fixed income investments—a major reason investing in online loans is becoming more desirable. Of course, actual returns will depend on what loans you invest in and the level of risk you take—typically the more risk you take on, the greater your potential return will be. At Lending Club, for instance, Grade-A loans have an adjusted net annualized return of 4.89%, compared with 9.11% for Grade-E loans, according to the company’s website.
Returns tend to be favorable compared with other fixed income investments—a major reason investing in online loans is becoming more desirable. Of course, actual returns will depend on what loans you invest in and the level of risk you take—typically the more risk you take on, the greater your potential return will be. At Lending Club, for instance, Grade-A loans have an adjusted net annualized return of 4.89%, compared with 9.11% for Grade-E loans, according to the company’s website.
To encourage more people to start investing, some savvy investors have started to self-publish online the quarterly returns they accumulate through the Lending Club and Prosper platforms. Renton, of Lend Academy, reported a balance of $476,769 on Dec. 31, 2014 and a real-world return for the trailing 12 months of 11.11 percent. Another well-known P2P investor and blogger, Simon Cunningham—the founder of LendingMemo Media in Seattle—reported a 12-month trailing return of 12.0 percent over the same time period, with a published account value of $41,496. Both investors say they expect returns to drop back somewhat over time, however, as the online marketplaces continue to lower interest rates to attract more borrowers.
Of course, if you’re an accredited investor, you will have access to even more online marketplaces. For instance, there’s SoFi of San Francisco for student loans, Realty Mogul of Los Angeles for real estate loans and Upstart of Palo Alto, California, that focuses on loans to people with thin or no credit history. The list of possibilities goes on and on.
Generally speaking, the more money you have to invest, the more options you have. “In this country today, you’ve got well over a hundred options if you’re willing to put seven figures in,” Renton says.
The minimums at venues that focus on accredited investors tend to be more than you’d find at Lending Club or Prosper. At SoFi, accredited investors need at least $10,000 to begin investing in the company’s unsecured corporate debt. SoFi’s been in the lending business for several years now and currently focuses on student loans, mortgages, personal loans and MBA loans. Investors, however, can’t currently invest in these loans, says Christina Kramlich, co-head of marketplace investments and investor relations at SoFi. The company plans to eventually offer investment opportunities in the areas of mortgages and personal loans, she says.
 At Funding Circle USA in San Francisco, accredited investors can buy into a limited partnership fund for at least $250,000. Or they can buy pieces of small business loans for a minimum of $1,000 each, though the recommended minimum is $50,000, explains Albert Periu, head of capital markets. There may also be upper limits on your investment, based on your financials. If you’re part of the pick-and-choose marketplace, you’ll pay an annual servicing fee of 1%. With the fund, you’ll also pay an administration fee of 1%. Trailing 12-month net returns for investors are north of 10%, Periu says.
At Funding Circle USA in San Francisco, accredited investors can buy into a limited partnership fund for at least $250,000. Or they can buy pieces of small business loans for a minimum of $1,000 each, though the recommended minimum is $50,000, explains Albert Periu, head of capital markets. There may also be upper limits on your investment, based on your financials. If you’re part of the pick-and-choose marketplace, you’ll pay an annual servicing fee of 1%. With the fund, you’ll also pay an administration fee of 1%. Trailing 12-month net returns for investors are north of 10%, Periu says.
Because it’s still so new, it can be hard for investors to know how to compare marketplaces. For starters, consider the platform’s historical performance. There are a lot of new marketplaces popping up, but it takes time to develop a proven track record. This isn’t to say you shouldn’t dabble with the newer platforms, but if you do, you’ll want above-average returns to balance out the higher risk, says Sanborn of Lending Club. “About three years in, we started to build a track record. At five years in, it was very solid,” he says. “You need time to see how a basic batch of loans is going to perform.”
Before investing, you’ll want to get a sense of how committed senior management is to the company and try and get a sense of whether the company seems to have enough capital for the business to run well. Try to find out about the cash position of the company, how the loans are going to be serviced, what entity is doing the underwriting and how and where your cash will be held.
“It’s not just assessing the risk of the asset and the investment, it’s assessing the risk of the enterprise that is making it available to you,” Sanborn says.
It’s also important to ask questions about the loans themselves. Where do they come from and is the volume sustainable? Ideally, a platform should offer a variety of loans so investors can properly diversify, or you might need to consider investing with multiple platforms to achieve your desired balance.
 Before you get started, you’ll also want to ask about the company’s compliance procedures and controls and how you can recover your money if you no longer want to invest. Data security is another area to explore. Not every company is as protective of customer data as perhaps they should be.
Before you get started, you’ll also want to ask about the company’s compliance procedures and controls and how you can recover your money if you no longer want to invest. Data security is another area to explore. Not every company is as protective of customer data as perhaps they should be.
When you’re asking all these questions, try to get a sense of how receptive the platform is to the feelers you’re putting out. Investors should only work with companies that are willing to be open about how they are investing your money, their historical returns and other important data. “I can’t stress transparency enough,” says Periu of Funding Circle.
The technology the platform uses is another key element. Is the technology easy to use, or does the platform create stumbling blocks for investors? Are there ways to automate lending, or do you have to log on every day and manually invest in loans?
Suber of Prosper says investors should also consider whether platforms work with a back-up servicer in case there’s a disruption and whether they run regular tests to make sure everything works as expected. “It’s just like a backup generator and you have to test it every once in a while and make sure it goes on.”
Certainly it pays to do your homework before you invest your hard-earned cash with an online platform. Ask around, attend industry conferences and absorb all you can from publicly available data. The good news is that there will probably be even more information for you to tap into as the industry continues to grow.
“Two years ago [marketplace lending] was very esoteric. A year ago it was still esoteric,” says Funding Circle’s Periu. Now, more and more investors are hearing about marketplace lending and want to make it part of their broader fixed income bucket. Even so, more has to happen for it to become a mainstream investment. “Awareness and education need to continue,” he says.
Once more people understand the extent of what’s out there, Suber of Prosper expects investing in online marketplaces will take off even more than it already has. “A lot of people still don’t know this as an investment opportunity,” he says.





























